Incorporation of 53BP1 into phase-separated bodies in cancer cells during aberrant mitosis
- PMID: 36606487
- PMCID: PMC10112977
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.260027
Incorporation of 53BP1 into phase-separated bodies in cancer cells during aberrant mitosis
Abstract
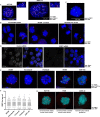
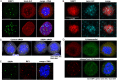
53BP1 (also known as TP53BP1) is a key mediator of the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) DNA repair pathway, which is the primary repair pathway in interphase cells. However, the mitotic functions of 53BP1 are less well understood. Here, we describe 53BP1 mitotic stress bodies (MSBs) formed in cancer cell lines in response to delayed mitosis. These bodies displayed liquid-liquid phase separation characteristics, were close to centromeres, and included lamin A/C and the DNA repair protein RIF1. After release from mitotic arrest, 53BP1 MSBs decreased in number and moved away from the chromatin. Using GFP fusion constructs, we found that the 53BP1 oligomerization domain region was required for MSB formation, and that inclusion of the 53BP1 N terminus increased MSB size. Exogenous expression of 53BP1 did not increase MSB size or number but did increase levels of MSB-free 53BP1. This was associated with slower mitotic progression, elevated levels of DNA damage and increased apoptosis, which is consistent with MSBs suppressing a mitotic surveillance by 53BP1 through sequestration. The 53BP1 MSBs, which were also found spontaneously in a subset of normally dividing cancer cells but not in non-transformed cells (ARPE-19), might facilitate the survival of cancer cells following aberrant mitoses. This article has an associated First Person interview with the first author of the paper.
Keywords: 53BP1; ARPE-19; Colon cancer cell lines; Lamin A/C; Mitotic arrest; Mitotic stress; RIF1.
© 2023. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Polo-like kinase 1 inhibits DNA damage response during mitosis.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(2):219-31. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.977067. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25607646 Free PMC article.
-
H4K20me2 distinguishes pre-replicative from post-replicative chromatin to appropriately direct DNA repair pathway choice by 53BP1-RIF1-MAD2L2.Cell Cycle. 2018;17(1):124-136. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1404210. Epub 2018 Jan 2. Cell Cycle. 2018. PMID: 29160738 Free PMC article.
-
Tumors overexpressing RNF168 show altered DNA repair and responses to genotoxic treatments, genomic instability and resistance to proteotoxic stress.Oncogene. 2017 Apr 27;36(17):2405-2422. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.392. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 27841863
-
Roles for 53BP1 in the repair of radiation-induced DNA double strand breaks.DNA Repair (Amst). 2020 Sep;93:102915. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102915. DNA Repair (Amst). 2020. PMID: 33087281 Review.
-
53BP1-mediated activation of the tumor suppressor p53.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2024 Dec;91:102424. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2024.102424. Epub 2024 Sep 7. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39244835 Review.
Cited by
-
Phase separation in DNA repair: orchestrating the cellular response to genomic stability.PeerJ. 2025 May 2;13:e19402. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19402. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40330699 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bond, M. J., Bleiler, M., Harrison, L. E., Scocchera, E. W., Nakanishi, M., G-Dayanan, N., Keshipeddy, S., Rosenberg, D. W., Wright, D. L. and Giardina, C. (2018). Spindle assembly disruption and cancer cell apoptosis with a CLTC-binding compound. Mol. Cancer Res. 16, 1361-1372. 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-18-0178 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

