Immunological effects and activity of multiple doses of zolbetuximab in combination with zoledronic acid and interleukin-2 in a phase 1 study in patients with advanced gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer
- PMID: 36607429
- PMCID: PMC10356865
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-022-04459-3
Immunological effects and activity of multiple doses of zolbetuximab in combination with zoledronic acid and interleukin-2 in a phase 1 study in patients with advanced gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Zolbetuximab (IMAB362) is engineered to induce antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity. We evaluated ADCC activity and the impact of the immune-modulating drugs zoledronic acid (ZA) and interleukin-2 (IL-2) as co-treatment with zolbetuximab on relevant immune cell populations and ADCC lysis activity.
Methods: This phase 1, multicenter, open-label study investigated the immunological effects and activity, safety, tolerability, and antitumor activity of multiple doses of zolbetuximab alone (n = 5) or in combination with ZA (n = 7) or with ZA plus two different dose levels of IL-2 (low dose: 1 million international units [mIU] [n = 9]; intermediate dose: 3 mIU [n = 7]) in pretreated patients with advanced gastric and gastroesophageal junction (G/GEJ) adenocarcinoma.
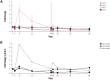
Results: Twenty-eight patients with previously treated advanced G/GEJ adenocarcinoma that was CLDN18.2-expressing were enrolled into four treatment arms. Treatment with zolbetuximab + ZA + IL-2 induced short-lived expansion and activation of ADCC-mediating cell populations, namely γ9δ2 T cells and natural killer cells, within 2 days after administration; this effect was more pronounced with intermediate-dose IL-2. Expansion and activation of regulatory T cells treated with either IL2 dose was moderate and short-lived. Strong ADCC activity was observed with zolbetuximab alone. Short-lived ADCC activity was observed in several patients treated with ZA + intermediate-dose IL-2, but not lower-dose IL-2. In the clinical efficacy population, the best confirmed response was stable disease (n = 11/19; 58%).
Conclusions: Zolbetuximab mediates proficient ADCC in patients with pretreated advanced G/GEJ cancers. Co-treatment with ZA + IL-2 did not further improve this effect.
Trial registration: NCT01671774.
Keywords: Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; Claudin 18.2; Esophagogastric junction cancer; Gastric cancer; Interleukin-2; Zolbetuximab.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
F Lordick reports study funding from Astellas Pharma, Inc.; grants from BMS and MSD (to institution); consulting fees from Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, BMS, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, MSD, Roche, and Zymeworks; payments or honoraria from Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, BMS, Eli Lilly, MSD, and Roche; travel support from BMS and Roche; advisory board participation for BioNTech; and leadership or fiduciary role in the European Society for Medical Oncology (unpaid) and the International Gastric Cancer Association (unpaid). P Thuss-Patience reports study funding from Astellas Pharma, Inc. and advisory board participation (outside the submitted work) with Lilly, BMS, MSD, Roche, Astellas Merck Serono, Servier, AstraZeneca, and Pfizer. M Bitzer reports study funding from Astellas Pharma, Inc. U Sahin is a co-founder and ex-shareholder of Ganymed Pharmaceuticals AG; he has also received consultancy fees from Ganymed Pharmaceuticals AG; he is also founder, chief executive officer, and a stockholder of BioNTech Holding, which is developing immunotherapies for cancer and other diseases. In addition, he has received consultancy fees from Astellas Pharma, Inc. and has pending, issued, and licensed patents relevant to the work, which have been acquired by Astellas Pharma, Inc. and for which he receives milestone payments. D Maurus reports study funding from Astellas Pharm, Inc. Ö Türeci is co-founder, chief executive officer, and an ex-shareholder of Ganymed Pharmaceuticals AG; she is also co-founder, chief medical officer and a stockholder of BioNTech Holding, which is developing immunotherapies for cancer and other diseases. In addition, she has received consultancy fees from Astellas Pharma, Inc. and has pending, issued, and licensed patents relevant to the work, which have been acquired by Astellas Pharma, Inc. and for which she receives milestone payments. All authors report management support from OPEN Health for manuscript development.
Figures





References
-
- Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A et al (2010) Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 376:687–697. 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61121-X - PubMed
-
- European Medicines Agency (2022a) Keytruda (pembrolizumab). Summary of product characteristics. Available at https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/keytruda-epar.... Accessed September 1, 2022a
-
- European Medicines Agency (2022b) Opdivo (nivolumab). Summary of product characteristics. Available at https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/opdivo-epar-p.... Accessed September 1, 2022b
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

