Impact of time to diagnosis on the occurrence of cardiogenic shock in MIS-C post-COVID-19 infection
- PMID: 36607546
- PMCID: PMC9817434
- DOI: 10.1007/s12519-022-00681-8
Impact of time to diagnosis on the occurrence of cardiogenic shock in MIS-C post-COVID-19 infection
Abstract
Background: In multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), diagnostic delay could be associated with severity. This study aims to measure the time to diagnosis in MIS-C, assess its impact on the occurrence of cardiogenic shock, and specify its determinants.
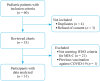
Methods: A single-center prospective cohort observational study was conducted between May 2020 and July 2022 at a tertiary care hospital. Children meeting the World Health Organization MIS-C criteria were included. A long time to diagnosis was defined as six days or more. Data on time to diagnosis were collected by two independent physicians. The primary outcome was the occurrence of cardiogenic shock. Logistic regression and receiver operating characteristic curve analysis were used for outcomes, and a Cox proportional hazards model was used for determinants.
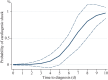
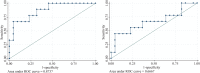
Results: Totally 60 children were assessed for inclusion, and 31 were finally analyzed [52% males, median age 8.8 (5.7-10.7) years]. The median time to diagnosis was 5.3 (4.2-6.2) days. In univariable analysis, age above the median, time to diagnosis, high C-reactive protein, and high N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) were associated with cardiogenic shock [odds ratio (OR) 6.13 (1.02-36.9), 2.79 (1.15-6.74), 2.08 (1.05-4.12), and 1.70 (1.04-2.78), respectively]. In multivariable analysis, time to diagnosis ≥ 6 days was associated with cardiogenic shock [adjusted OR (aOR) 21.2 (1.98-227)]. Time to diagnosis ≥ 6 days had a sensitivity of 89% and a specificity of 77% in predicting cardiogenic shock; the addition of age > 8 years and NT-proBNP at diagnosis ≥ 11,254 ng/L increased the specificity to 91%. Independent determinants of short time to diagnosis were age < 8.8 years [aHR 0.34 (0.13-0.88)], short distance to tertiary care hospital [aHR 0.27 (0.08-0.92)], and the late period of the COVID-19 pandemic [aHR 2.48 (1.05-5.85)].
Conclusions: Time to diagnosis ≥ 6 days was independently associated with cardiogenic shock in MIS-C. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to avoid the use of inotropes and limit morbidity, especially in older children.
Keywords: COVID-19; Delay in diagnosis; Heart failure; MIS-C; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2023. Children's Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
No financial or non-financial benefits have been received or will be received from any party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Figures
References
-
- SPF. Situation épidémiologique liée à la COVID-19 chez les 0–17 ans. Point au 7 juillet 2022. https://www.santepubliquefrance.fr/maladies-et-traumatismes/maladies-et-.... Accessed 20 Aug 2022
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

