Protocol to analyze bioenergetics in single human induced-pluripotent-stem-cell-derived kidney organoids using Seahorse XF96
- PMID: 36607813
- PMCID: PMC9850189
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2022.101999
Protocol to analyze bioenergetics in single human induced-pluripotent-stem-cell-derived kidney organoids using Seahorse XF96
Abstract
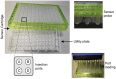
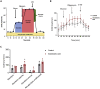
Metabolic derangement is a key culprit in kidney pathophysiology. Organoids have emerged as a promising in vitro tool for kidney research. Here, we present a fine-tuned protocol to analyze bioenergetics in single human induced-pluripotent-stem-cell (iPSC)-derived kidney organoids using Seahorse XF96. We describe the generation of self-organized three-dimensional kidney organoids, followed by preparation of organoids for Seahorse XF96 analysis. We then detail how to carry out stress tests to determine mitochondrial and glycolytic rates in single kidney organoids.
Keywords: Cell Differentiation; Metabolism; Organoids; Stem Cells.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Jansen J., Reimer K.C., Nagai J.S., Varghese F.S., Overheul G.J., de Beer M., Roverts R., Daviran D., Fermin L.A.S., Willemsen B., et al. SARS-CoV-2 infects the human kidney and drives fibrosis in kidney organoids. Cell Stem Cell. 2022;29:217–231.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2021.12.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

