Association between zinc deficiency and aorta stiffness in non-diabetic hemodialysis patients
- PMID: 36607966
- PMCID: PMC9821515
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268875
Association between zinc deficiency and aorta stiffness in non-diabetic hemodialysis patients
Abstract
Objectives: Zinc deficiency (Zn < 60 μg/dL) is known to play an important role for vascular calcification. However, little data is available regarding the association between zinc deficiency and aorta stiffness in dialysis patients. Thus, we studied the relationship between zinc deficiency and aorta stiffness in non-diabetic hemodialysis (HD) patients.
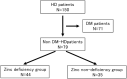
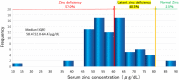
Methods: Of 150 patients receiving maintenance HD at our hospital, we included 79 non-diabetic HD patients (age: 70±11 years, 49 men) after excluding 71 diabetic HD patients. Zinc deficiency was defined as Zn <60 μg/dL during pre-HD blood sampling. The association between zinc deficiency and aorta stiffness was analyzed. Aorta stiffness was evaluated as brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV). Other surrogate markers for cardiovascular complications were also measured.
Results: The zinc deficiency group (ZD group) included 45 patients (57.0%). Compared to the zinc non-deficiency group (ZND group), patients with ZD group were significantly older, higher levels of CRP and hypoalbuminemia. Moreover, they had significantly higher levels of baPWV, and lower levels of ankle-brachial pressure index (ABI) (p<0.05). After adjusting for hypoalbuminemia, and CRP, multivariate analysis showed that age and zinc level were independent predictors of baPWV.
Conclusion: The study suggested that zinc deficiency may be an independent risk factor for aorta stiffness, even after adjusting for malnutrition and inflammation.
Copyright: © 2023 Ishioka et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Sarnak MJ. Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998; 9(12 Suppl): S16–S23. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

