PHF5A facilitates the development and progression of gastric cancer through SKP2-mediated stabilization of FOS
- PMID: 36609277
- PMCID: PMC9817416
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-022-03821-w
PHF5A facilitates the development and progression of gastric cancer through SKP2-mediated stabilization of FOS
Abstract
Background: Gastric cancer (GC) is the fifth most common cancer and the third most common cause of cancer death worldwide. Plant homeodomain (PHD)-finger domain protein PHF5A has been demonstrated to play a promoting role in a variety of cancers. This study aimed to clarify the role of PHF5A in the progression of GC and its potential mechanism of action.
Methods: Immunohistochemical staining experiments were performed based on tissues from clinical GC patients to reveal PHF5A expression. A series of functional experiments in vitro and in vivo were used to clarify the role of PHF5A in GC.
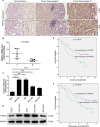
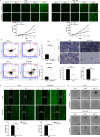
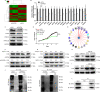
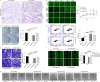
Results: Clinically, PHF5A was abundantly expressed in GC and existed clinical value indicating poor prognosis. In addition, GC cells with knockdown of PHF5A expression showed slowed proliferation, enhanced sensitivity to apoptosis and inhibition of migration. Mechanically, knockdown of PHF5A led to decreased protein stability of FOS, which was mediated ubiquitination of E3 ubiquitin ligase S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (SKP2). Moreover, downregulation of FOS attenuated the promotion of PHF5A overexpression on GC cells. Consistently, Pladienolide B (PHF5A inhibitor) treatment reversed the induction of PHF5A overexpression on the malignant phenotypes and tumor formation of GC cells.
Conclusion: Knockdown of PHF5A inhibited the progression of GC through SKP2-mediated ubiquitination of FOS, which may be a promising candidate target with potential therapeutic value.
Keywords: FOS; Gastric cancer; PHF5A; Phenotype; Ubiquitination.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PHD finger protein 5A promoted lung adenocarcinoma progression via alternative splicing.Cancer Med. 2019 May;8(5):2429-2441. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2115. Epub 2019 Apr 1. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 30932358 Free PMC article.
-
Thioridazine reverses trastuzumab resistance in gastric cancer by inhibiting S-phase kinase associated protein 2-mediated aerobic glycolysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Dec 7;29(45):5974-5987. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i45.5974. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 38130998 Free PMC article.
-
PHF5A Contributes to the Maintenance of the Cancer Stem-like Phenotype in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Regulating Histone Deacetylase 8.Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2022 May;52(3):439-451. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2022. PMID: 35777798
-
Plant homeodomain-finger protein 5A: A key player in cancer progression.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Dec 31;169:115857. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115857. Epub 2023 Nov 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37951028 Review.
-
Research progress and therapeutic prospect of PHF5A acting as a new target for malignant tumors.Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Nov 25;51(5):647-655. doi: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2022-0459. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 36581580 Free PMC article. Review. English.
Cited by
-
PHF5A is a potential diagnostic, prognostic, and immunological biomarker in pan-cancer.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 16;13(1):17521. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44899-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37845358 Free PMC article.
-
Implication of protein post translational modifications in gastric cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Feb 4;13:1523958. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1523958. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 39968176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive analysis of PHF5A as a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target across cancers and in hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2024 Jul 19;24(1):868. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12620-z. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39030507 Free PMC article.
-
A real-world study and network pharmacology analysis of EGFR-TKIs combined with ZLJT to delay drug resistance in advanced lung adenocarcinoma.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Nov 21;23(1):422. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04213-3. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37990309 Free PMC article.
-
PHF5A promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via stabilizing VEGFA.Biol Direct. 2024 Mar 1;19(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s13062-023-00440-3. Biol Direct. 2024. PMID: 38429756 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

