Understanding the rise in traditional contraceptive methods use in Uttar Pradesh, India
- PMID: 36609308
- PMCID: PMC9817250
- DOI: 10.1186/s12978-022-01547-y
Understanding the rise in traditional contraceptive methods use in Uttar Pradesh, India
Abstract
Background: The sustainable development goals (SDG) aim at satisfying three-fourths of family planning needs through modern contraceptive methods by 2030. However, the traditional methods (TM) of family planning use are on the rise, along with modern contraception in Uttar Pradesh (UP), the most populous Indian state. This study attempts to explore the dynamics of rising TM use in the state.
Methods: We used a state representative cross-sectional survey conducted among 12,200 Currently Married Women (CMW) aged 15-49 years during December 2020-February 2021 in UP. Using a multistage sampling technique, 508 primary sampling units (PSU) were selected. These PSU were ASHA areas in rural settings and Census Enumeration Blocks in urban settings. About 27 households from each PSU were randomly selected. All the eligible women within the selected households were interviewed. The survey also included the nearest public health facilities to understand the availability of family planning methods. Univariate and bivariate analyses were conducted. Appropriate sampling weights were applied.
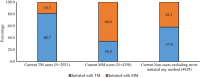
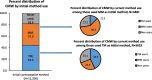
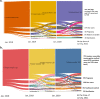
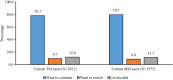
Results: Overall, 33.9% of CMW were using any modern methods and 23.7% any TM (Rhythm and withdrawal) at the time of survey. The results show that while the modern method use has increased by 2.2 percentage points, the TM use increased by 9.9 percentage points compared to NFHS-4 (2015-16). The use of TM was almost same across women of different socio-demographic characteristics. Of 2921 current TM users, 80.7% started with TM and 78.3% expressed to continue with the same in future. No side effects (56.9%), easy to use (41.7%) and no cost incurred (38.0%) were the main reasons for the continuation of TM. TM use increased despite a significant increase (66.1 to 81.3%) in the availability of modern reversible methods and consistent availability of limiting methods (84.0%) in the nearest public health facilities.
Conclusion: Initial contraceptive method was found to have significant implications for current contraceptive method choice and future preferences. Program should reach young and zero-parity women with modern method choices by leveraging front-line workers in rural UP. Community and facility platforms can also be engaged in providing modern method choices to women of other parities to increase modern contraceptive use further to achieve the SDG goals.
Keywords: Consistent use; FP method availability; Initial contraceptive method; Traditional methods; Uttar Pradesh.
Plain language summary
In Uttar Pradesh, the use of traditional methods of contraception is on the rise, observed similarly in many other Indian states in recent times. The emphasis on modern contraceptive methods and the rise and high prevalence of traditional method use in the state call for a systematic assessment to understand the dynamics such as patterns, prevalence and reasons for traditional method use for better family planning programming. Using a state representative cross-sectional survey data from Uttar Pradesh, we attempted to understand the dynamics of increasing traditional methods use. We found no significant variations in use of traditional methods by their socio-demographic characteristics. Not only that, most current traditional method users reported that their first method was a traditional method and an overwhelming proportion of women (4/5 traditional methods users) expressed to continue with the same method in future. Also the findings reveal that more than half of the traditional method users used the method consistently over the three-years calendar period. Among those who had unmet need at the time of survey, a considerable proportion of them intend to use traditional methods in future. This emphasized the importance of initial contraceptive method choice on current contraceptive use and future preference. Traditional methods use increased in the state despite a significant increase (66.1 to 81.3% during 2018 to 2021) in availability of modern reversible methods and consistent availability of limiting method (84.0%) in public health facilities.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Geographic and socioeconomic inequalities in the coverage of contraception in Uttar Pradesh, India.Reprod Health. 2024 Apr 11;21(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12978-024-01784-3. Reprod Health. 2024. PMID: 38600560 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiological models and related simulation results for understanding of contraceptive adoption in India.Int J Epidemiol. 2000 Apr;29(2):300-7. doi: 10.1093/ije/29.2.300. Int J Epidemiol. 2000. PMID: 10817129
-
Unmet need for family planning services among young married women (15-24 years) living in urban slums of India.BMC Womens Health. 2020 Sep 3;20(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s12905-020-01010-9. BMC Womens Health. 2020. PMID: 32883262 Free PMC article.
-
Engaging Community Health Workers to Enhance Modern Contraceptive Uptake Among Young First-Time Parents in Five Cities of Uttar Pradesh.Glob Health Sci Pract. 2024 May 21;12(Suppl 2):e2200170. doi: 10.9745/GHSP-D-22-00170. Print 2024 May 21. Glob Health Sci Pract. 2024. PMID: 38575360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accessibility and uptake of modern contraceptive methods in Pakistan - a critical view on what works?J Pak Med Assoc. 2021 Nov;71(Suppl 7)(11):S20-S32. J Pak Med Assoc. 2021. PMID: 34793425 Review.
Cited by
-
Voices unveiled: a mixed-methods exploration of family planning education, access, and Sociocultural determinants for enhancing contraceptive decision-making in western Gujarat, India.Contracept Reprod Med. 2025 Mar 31;10(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s40834-025-00362-7. Contracept Reprod Med. 2025. PMID: 40165338 Free PMC article.
-
Barriers to modern contraceptive use by female workers in Indonesia's urban areas.Korean J Fam Med. 2025 Jul;46(4):240-246. doi: 10.4082/kjfm.24.0005. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Korean J Fam Med. 2025. PMID: 38886147 Free PMC article.
-
Geographic and socioeconomic inequalities in the coverage of contraception in Uttar Pradesh, India.Reprod Health. 2024 Apr 11;21(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12978-024-01784-3. Reprod Health. 2024. PMID: 38600560 Free PMC article.
-
Oura Ring as a Tool for Ovulation Detection: Validation Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jan 31;27:e60667. doi: 10.2196/60667. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 39889300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Planning Commission G of I. Ninth five year plan: human and social development. https://niti.gov.in/planningcommission.gov.in/docs/plans/planrel/fiveyr/.... Accessed 26 Apr 2022.
-
- Maharatna A. India ’ s Family Planning Programme : an unpleasant essay. Econ Polit Wkly. 2010;37(10):971–981.
-
- United Nations. Official list of MDG indicators. https://millenniumindicators.un.org/unsd/mdg/Host.aspx?Content=Indicator.... Accessed 26 Apr 2022.
-
- United Nations & Niti Aayog. SDG India Index and Dashboard 2019. 2019;181. https://niti.gov.in/sites/default/files/2019-12/SDG-India-Index-2.0_27-D....
-
- National Commission Population and Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. Population projections for India and states 2011–2036, Report of the technical group on population projections. Nirman Bhawan, New Delhi-110011; 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

