A phase II study of palbociclib plus letrozole plus trastuzumab as neoadjuvant treatment for clinical stages II and III ER+ HER2+ breast cancer (PALTAN)
- PMID: 36609389
- PMCID: PMC9822956
- DOI: 10.1038/s41523-022-00504-z
A phase II study of palbociclib plus letrozole plus trastuzumab as neoadjuvant treatment for clinical stages II and III ER+ HER2+ breast cancer (PALTAN)
Abstract
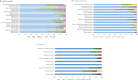
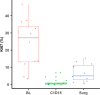
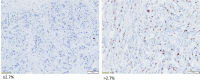
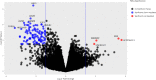
Patients with ER+/HER2+ breast cancer (BC) are less likely to achieve pathological complete response (pCR) after chemotherapy with dual HER2 blockade than ER-/HER2+ BC. Endocrine therapy plus trastuzumab is effective in advanced ER+/HER2+ BC. Inhibition of CDK4/6 and HER2 results in synergistic cell proliferation reduction. We combined palbociclib, letrozole, and trastuzumab (PLT) as a chemotherapy-sparing regimen. We evaluated neoadjuvant PLT in early ER+/HER2+ BC. Primary endpoint was pCR after 16 weeks. Research biopsies were performed for whole exome and RNA sequencing, PAM50 subtyping, and Ki67 assessment for complete cell cycle arrest (CCCA: Ki67 ≤ 2.7%). After 26 patients, accrual stopped due to futility. pCR (residual cancer burden-RCB 0) was 7.7%, RCB 0/I was 38.5%. Grade (G) 3/4 treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 19. Among these, G3/4 neutropenia was 50%, hypertension 26.9%, and leucopenia 7.7%. Analysis indicated CCCA in 85% at C1 day 15 (C1D15), compared to 27% at surgery after palbociclib was discontinued. Baseline PAM50 subtyping identified 31.2% HER2-E, 43.8% Luminal B, and 25% Luminal A. 161 genes were differentially expressed comparing C1D15 to baseline. MKI67, TK1, CCNB1, AURKB, and PLK1 were among the genes downregulated, consistent with CCCA at C1D15. Molecular Signatures Database gene-sets analyses demonstrated downregulated processes involved in proliferation, ER and mTORC1 signaling, and DNA damage repair at C1D15, consistent with the study drug's mechanisms of action. Neoadjuvant PLT showed a pCR of 7.7% and an RCB 0/I rate of 38.5%. RNA sequencing and Ki67 data indicated potent anti-proliferative effects of study treatments. ClinicalTrials.gov- NCT02907918.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests but the following competing interests. F.O.A. receives research funding from Pfizer, Immunomedics, NeoImmuneTech, RNA Diagnostics, and Astellas, and fees from Teladoc Health, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, QED Therapeutics, Immunomedics, Cardinal Health, Athenex, Gilead, and Biotheranostics. C.X.M. receives research funding from Pfizer and Puma Biotechnology, Inc., and fees from AstraZeneca, Jacobio, Pfizer, Natera, Novartis, Inivata, Biovica, Athenex, Sanofi, Bayer, Seattle Genetics, Eisai.
Figures


References
-
- Gianni L, et al. Efficacy and safety of neoadjuvant pertuzumab and trastuzumab in women with locally advanced, inflammatory, or early HER2-positive breast cancer (NeoSphere): a randomised multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:25–32. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70336-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schneeweiss A, et al. Pertuzumab plus trastuzumab in combination with standard neoadjuvant anthracycline-containing and anthracycline-free chemotherapy regimens in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer: a randomized phase II cardiac safety study (TRYPHAENA) Ann. Oncol. 2013;24:2278–2284. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt182. - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

