The N6-methyladenosine METTL3 regulates tumorigenesis and glycolysis by mediating m6A methylation of the tumor suppressor LATS1 in breast cancer
- PMID: 36609396
- PMCID: PMC9824909
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-022-02581-1
The N6-methyladenosine METTL3 regulates tumorigenesis and glycolysis by mediating m6A methylation of the tumor suppressor LATS1 in breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Posttranscriptional modification of tumor-associated factors plays a pivotal role in breast cancer progression. However, the underlying mechanism remains unknown. M6A modifications in cancer cells are dynamic and reversible and have been found to impact tumor initiation and progression through various mechanisms. In this study, we explored the regulatory mechanism of breast cancer cell proliferation and metabolism through m6A methylation in the Hippo pathway. METHODS: A combination of MeRIP-seq, RNA-seq and metabolomics-seq was utilized to reveal a map of m6A modifications in breast cancer tissues and cells. We conducted RNA pull-down assays, RIP-qPCR, MeRIP-qPCR, and RNA stability analysis to identify the relationship between m6A proteins and LATS1 in m6A regulation in breast cancer cells. The expression and biological functions of m6A proteins were confirmed in breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, we investigated the phosphorylation levels and localization of YAP/TAZ to reveal that the activity of the Hippo pathway was affected by m6A regulation of LATS1 in breast cancer cells. RESULTS: We demonstrated that m6A regulation plays an important role in proliferation and glycolytic metabolism in breast cancer through the Hippo pathway factor, LATS1. METTL3 was identified as the m6A writer, with YTHDF2 as the reader protein of LATS1 mRNA, which plays a positive role in promoting both tumorigenesis and glycolysis in breast cancer. High levels of m6A modification were induced by METTL3 in LATS1 mRNA. YTHDF2 identified m6A sites in LATS1 mRNA and reduced its stability. Knockout of the protein expression of METTL3 or YTHDF2 increased the expression of LATS1 mRNA and suppressed breast cancer tumorigenesis by activating YAP/TAZ in the Hippo pathway.
Conclusions: In summary, we discovered that the METTL3-LATS1-YTHDF2 pathway plays an important role in the progression of breast cancer by activating YAP/TAZ in the Hippo pathway.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Hippo-YAP/TAZ signaling pathway; LATS1; METTL3.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Youqin Xu, Mu Song, Ziyang Hong, Wancheng Chen, Qianbing Zhang, Jianlong Zhou, Chao Yang, Zilong He, Juanjuan Yu, Xiaolin Peng, Qiuhong Zhu, Shaotian Li, Kaiyuan Ji, Minfeng Liu and Qiang Zuo declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



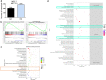
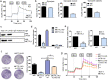
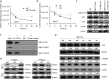
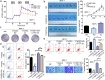
References
-
- Denkert C, von Minckwitz G, Darb-Esfahani S, Lederer B, Heppner BI, Weber KE, Budczies J, Huober J, Klauschen F, Furlanetto J, et al. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and prognosis in different subtypes of breast cancer: a pooled analysis of 3771 patients treated with neoadjuvant therapy. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(1):40–50. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30904-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022;12(1):31–46. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1059. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

