Lung Transplantation for Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
- PMID: 36610665
- PMCID: PMC10206512
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chest.2022.12.032
Lung Transplantation for Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Abstract
Background: Patients with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) have poor respiratory trajectories and are at increased risk of lung function decline with age. Lung transplant (LTx) is a possible treatment option for this growing patient population, but little has been published on LTx in this patient group.
Research question: What are the characteristics of patients with BPD who are listed for LTx? How do waitlist and post-LTx outcomes for BPD compare with LTx for other diagnoses?
Study design and methods: The United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) registry was queried for patients of all ages listed for or who underwent LTx (2000-2020). Descriptive analysis, waitlist outcomes, and post-LTx survival at 1, 5, and 10 years were assessed comparing patients with BPD vs LTx patients with other diagnoses. Post-LTx survival for patients with BPD born in the pre-surfactant era (pre-SE, before 1990) and those born in the post-surfactant era (post-SE) was compared. Propensity score matching was performed to control for the risk factors and match patients with BPD with other LTx patients on a 1:1 ratio.
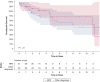
Results: BPD was reported in 65 patients, of whom 32 (49.2%) underwent LTx. Patients with BPD at listing were younger than those with other diagnoses (median age, 21 [interquartile range, 5-31] years vs 57 [45-63] years; P < .001), and more were likely to receive mechanical ventilation at listing (23% vs 3.7%; P < .001). Patients with BPD had an FEV1 of 17% compared with 34% predicted in other patients (P = .002). Patients with BPD had an overall similar post-LTx survival compared with patients with other diagnoses (P = .106), even following propensity score matching (P = .41).
Interpretation: LTx for BPD has increased over the last 20 years. Patients with BPD have similar post-LTx outcomes compared with those of other patient populations in the modern era. Thus, LTx could be considered for patients with BPD experiencing progressive respiratory deterioration.
Keywords: COPD; bronchopulmonary dysplasia; lung transplant.
Copyright © 2023 American College of Chest Physicians. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Bhandari A., McGrath-Morrow S. Long-term pulmonary outcomes of patients with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Perinatol. 2013;37(2):132–137. - PubMed
-
- Northway W.H., Jr., Rosan R.C., Porter D.Y. Pulmonary disease following respirator therapy of hyaline-membrane disease. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 1967;276(7):357–368. - PubMed
-
- Husain A.N., Siddiqui N.H., Stocker J.T. Pathology of arrested acinar development in postsurfactant bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Hum Pathol. 1998;29(7):710–717. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

