Early response evaluation by single cell signaling profiling in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 36611026
- PMCID: PMC9825407
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-35624-4
Early response evaluation by single cell signaling profiling in acute myeloid leukemia
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Early response evaluation by single cell signaling profiling in acute myeloid leukemia.Nat Commun. 2023 Mar 30;14(1):1767. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37488-8. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36997540 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
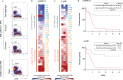
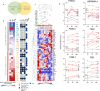
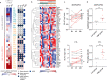
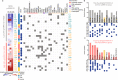
Aberrant pro-survival signaling is a hallmark of cancer cells, but the response to chemotherapy is poorly understood. In this study, we investigate the initial signaling response to standard induction chemotherapy in a cohort of 32 acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients, using 36-dimensional mass cytometry. Through supervised and unsupervised machine learning approaches, we find that reduction of extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation in the myeloid cell compartment 24 h post-chemotherapy is a significant predictor of patient 5-year overall survival in this cohort. Validation by RNA sequencing shows induction of MAPK target gene expression in patients with high phospho-ERK1/2 24 h post-chemotherapy, while proteomics confirm an increase of the p38 prime target MAPK activated protein kinase 2 (MAPKAPK2). In this study, we demonstrate that mass cytometry can be a valuable tool for early response evaluation in AML and elucidate the potential of functional signaling analyses in precision oncology diagnostics.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

