Foot orthoses for flexible flatfeet in children and adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of patient-reported outcomes
- PMID: 36611153
- PMCID: PMC9825043
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-022-06044-8
Foot orthoses for flexible flatfeet in children and adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of patient-reported outcomes
Abstract
Background: This systematic review and meta-analysis examined the effectiveness of orthoses for flexible flatfeet in terms of patient-reported outcomes in children and adults.
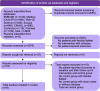
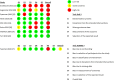
Methods: EMBASE, Medline (OvidSP), Web-of-Science, Scopus, CINAHL, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Clinical Trials, i.e., Cochrane Central and Pubmed were searched to identify relevant studies since their inception up to February 2021. We included randomized controlled trials (RCT) and prospective studies in which patient reported outcomes at baseline and follow-up in an orthoses group were compared with a no orthoses or sham sole group. Methodological quality of the studies was assessed using the Revised Cochrane risk-of-bias tool for randomized trials (RoB 2) and the Risk Of Bias In Non-Randomized Studies of Interventions (ROBINS-I). A meta-analysis was performed where there were multiple studies with the same outcome measures, which was the case for the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) for pain in adults.
Results: In total nine studies were included: four RCT in children (N = 353) and four RCT and one prospective study in adults (N = 268) were included. There was considerable heterogeneity between studies. A meta-analysis demonstrated that pain reduction between baseline and follow-up was significantly larger in the orthoses (N = 167) than in the control groups in adults (N = 157; - 4.76, 95% CI [- 9.46, - 0.06], p0.05).
Conclusion: Due to heterogeneity in study designs, we cannot conclude that foot orthoses are useful for flexible flatfoot in children and adults. However, based on the meta-analysis orthoses might be useful in decreasing pain in adults. The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Keywords: Adults; Children; Foot orthoses; Meta-analysis; Symptomatic flexible flatfeet; Systematic review.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article. All authors have nothing to disclose. The manuscript submitted does not contain information about medical device(s)/drug(s).
Figures

References
-
- Michaudet C, Edenfield KM, Nicolette GW, Carek PJ. Foot and Ankle Conditions: Pes Planus. FP Essent. 2018;465:18–23. - PubMed
-
- Michaudet C, Edenfield KM, Nicolette GW, Carek PJ. Foot and Ankle Conditions: Pes Planus. FP Essent. 2018;465:18–23. - PubMed
-
- Evans AM, Rome K. A Cochrane review of the evidence for non-surgical interventions for flexible pediatric flat feet. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2011;47:69–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

