The gyrfalcon (Falco rusticolus) genome
- PMID: 36611193
- PMCID: PMC9997569
- DOI: 10.1093/g3journal/jkad001
The gyrfalcon (Falco rusticolus) genome
Abstract
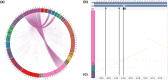
High-quality genome assemblies are characterized by high-sequence contiguity, completeness, and a low error rate, thus providing the basis for a wide array of studies focusing on natural species ecology, conservation, evolution, and population genomics. To provide this valuable resource for conservation projects and comparative genomics studies on gyrfalcon (Falco rusticolus), we sequenced and assembled the genome of this species using third-generation sequencing strategies and optical maps. Here, we describe a highly contiguous and complete genome assembly comprising 20 scaffolds and 13 contigs with a total size of 1.193 Gbp, including 8,064 complete Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs (BUSCOs) of the total 8,338 BUSCO groups present in the library aves_odb10. Of these BUSCO genes, 96.7% were complete, 96.1% were present as a single copy, and 0.6% were duplicated. Furthermore, 0.8% of BUSCO genes were fragmented and 2.5% (210) were missing. A de novo search for transposable elements (TEs) identified 5,716 TEs that masked 7.61% of the F. rusticolus genome assembly when combined with publicly available TE collections. Long interspersed nuclear elements, in particular, the element Chicken-repeat 1 (CR1), were the most abundant TEs in the F. rusticolus genome. A de novo first-pass gene annotation was performed using 293,349 PacBio Iso-Seq transcripts and 496,195 transcripts derived from the assembly of 42,429,525 Illumina PE RNA-seq reads. In all, 19,602 putative genes, of which 59.31% were functionally characterized and associated with Gene Ontology terms, were annotated. A comparison of the gyrfalcon genome assembly with the publicly available assemblies of the domestic chicken (Gallus gallus), zebra finch (Taeniopygia guttata), and hummingbird (Calypte anna) revealed several genome rearrangements. In particular, nine putative chromosome fusions were identified in the gyrfalcon genome assembly compared with those in the G. gallus genome assembly. This genome assembly, its annotation for TEs and genes, and the comparative analyses presented, complement and strength the base of high-quality genome assemblies and associated resources available for comparative studies focusing on the evolution, ecology, and conservation of Aves.
Keywords: Falco rusticolus; CR1; chromosome fusion; conservation genomics; gyrfalcon; long reads; transposable elements.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Genetics Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest None declared.
Figures


References
-
- BioBam . 2019. OmicsBox–Bioinformatics made easy. https://www.biobam.com/omicsbox.
-
- Bravo GA, Schmitt CJ, Scott VE. What have we learned from the first 500 avian genomes? . Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst. 2021;52(1):611–639. doi:10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-012121-085928. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
