Left Ventricular Fibrosis Assessment by Native T1, ECV, and LGE in Pulmonary Hypertension Patients
- PMID: 36611364
- PMCID: PMC9818262
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13010071
Left Ventricular Fibrosis Assessment by Native T1, ECV, and LGE in Pulmonary Hypertension Patients
Abstract
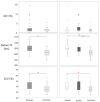
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is emerging as an alternative to right heart catheterization for the evaluation of pulmonary hypertension (PH) patients. The aim of this study was to compare cardiac MRI-derived left ventricle fibrosis indices between pre-capillary PH (PrePH) and isolated post-capillary PH (IpcPH) patients and assess their associations with measures of ventricle function. Global and segmental late gadolinium enhancement (LGE), longitudinal relaxation time (native T1) maps, and extracellular volume fraction (ECV) were compared among healthy controls (N = 25; 37% female; 52 ± 13 years), PH patients (N = 48; 60% female; 60 ± 14 years), and PH subgroups (PrePH: N = 29; 65% female; 55 ± 12 years, IpcPH: N = 19; 53% female; 66 ± 13 years). Cardiac cine measured ejection fraction, end diastolic, and end systolic volumes and were assessed for correlations with fibrosis. LGE mural location was qualitatively assessed on a segmental basis for all subjects. PrePH patients had elevated (apical-, mid-antero-, and mid-infero) septal left ventricle native T1 values (1080 ± 74 ms, 1077 ± 39 ms, and 1082 ± 47 ms) compared to IpcPH patients (1028 ± 53 ms, 1046 ± 36 ms, 1051 ± 44 ms) (p < 0.05). PrePH had a higher amount of insertional point LGE (69%) and LGE patterns characteristic of non-vascular fibrosis (77%) compared to IpcPH (37% and 46%, respectively) (p < 0.05; p < 0.05). Assessment of global LGE, native T1, and ECV burdens did not show a statistically significant difference between PrePH (1.9 ± 2.7%, 1056.2 ± 36.3 ms, 31.2 ± 3.7%) and IpcPH (2.7 ± 2.7%, 1042.4 ± 28.1 ms, 30.7 ± 4.7%) (p = 0.102; p = 0.229 p = 0.756). Global native T1 and ECV were higher in patients (1050.9 ± 33.8 and 31.0 ± 4.1%) than controls (28.2 ± 3.7% and 1012.9 ± 29.4 ms) (p < 0.05). Cardiac MRI-based tissue characterization may augment understanding of cardiac involvement and become a tool to facilitate PH patient classification.
Keywords: extracellular volume fraction; late gadolinium enhancement; native T1; pulmonary hypertension.
Conflict of interest statement
J.C.C. is the principal investigator for this Bayer funded study. He declares that he has previously participated in advisory boards for Bayer, Guerbet, and Bracco. He participates in speaking roles sponsored by Bayer. He has received institutional research support sponsored by Bayer, Guerbet, and Siemens. M.M. has received research support from Siemens. He has received research grants from Circle Cardiovascular imaging and Cryolife incorporated. B.D.A. and R.J.A. have performed consulting for Circle Cardiovascular Imaging. K.C. is a full-time employee of Siemens. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Potential Prognostic Value of Native T1 in Pulmonary Hypertension Patients.Life (Basel). 2023 Mar 13;13(3):775. doi: 10.3390/life13030775. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36983931 Free PMC article.
-
T1-Mapping and extracellular volume estimates in pediatric subjects with Duchenne muscular dystrophy and healthy controls at 3T.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2020 Dec 10;22(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12968-020-00687-z. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2020. PMID: 33302967 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Involvement in Patients Recovered From COVID-2019 Identified Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020 Nov;13(11):2330-2339. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2020.05.004. Epub 2020 May 12. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32763118 Free PMC article.
-
Native T1 Mapping, Extracellular Volume Mapping, and Late Gadolinium Enhancement in Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Meta-Analysis.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020 Jun;13(6):1299-1310. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2020.03.010. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32498919 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Non-late Gadolinium Enhancement Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Parameters in Cardiac Amyloidosis.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2023 Apr;48(4):101573. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2022.101573. Epub 2022 Dec 28. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 36586704 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Prognostic Value of Native T1 in Pulmonary Hypertension Patients.Life (Basel). 2023 Mar 13;13(3):775. doi: 10.3390/life13030775. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36983931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Masci P.G., Doulaptsis C., Bertella E., Del Torto A., Symons R., Pontone G., Barison A., Droogné W., Andreini D., Lorenzoni V., et al. Incremental Prognostic Value of Myocardial Fibrosis in Patients with Non–Ischemic Cardiomyopathy without Congestive Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2014;7:448–456. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.113.000996. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tandon A., Villa C.R., Hor K.N., Jefferies J.L., Gao Z., Towbin J.A., Wong B.L., Mazur W., Fleck R.J., Sticka J.J., et al. Myocardial Fibrosis Burden Predicts Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction and Is Associated with Age and Steroid Treatment Duration in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015;4:e001338. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.114.001338. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li A., Poon J.W., Ching S., Chan K., Chung T., Yue C., Ha S.C., Chang H., Ng M. Pulmonary pressure-to-longitudinal strain ratio by echocardiography: A rapid surrogate to magnetic resonance for right ventricular failure assessment. Eur. Heart J.-Cardiovasc. Imaging. 2021;22:jeaa356.398. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jeaa356.398. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

