Cardiac Involvement in Children Affected by COVID-19: Clinical Features and Diagnosis
- PMID: 36611412
- PMCID: PMC9818331
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13010120
Cardiac Involvement in Children Affected by COVID-19: Clinical Features and Diagnosis
Abstract
COVID-19 (Coronavirus disease 2019) in children is usually mild. However, multiple organ disorders associated with SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2) have been detected with poor respiratory symptoms. Cardiac changes are noted in 17% to 75% of cases, which are associated with diagnostic difficulties in high-risk groups for the development of complications that are associated with myocardial damage by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The objective of this review is to identify the most significant symptoms of cardiac involvement affected by COVID-19, which require in-depth examination. The authors analyzed publications from December 2019 to the October 2022, which were published in accessible local and international databases. According to the analysis data, the main sign of myocardial involvement was increasing as cardiomarkers in the patient's blood, in particular troponin I or troponin T. Many authors noted that the increased level of CRP (C-reactive protein) and NT-proBNP, which are accompanied by changes in the ECG (electrocardiogram) and EchoCG (echocardiography), as a rule, were nonspecific. However, the identified cardiac functional dysfunctions affected by SARS-CoV-2, required an cardiac MRI. The lack of timely diagnosis of myocardial involvements, especially in children at high risk for the development of complications associated with SARS-CoV-2 myocardial injury, can lead to death. The direct damage of the structural elements of myocardial blood vessels in patients with severe hypoxic changes resulted from respiratory failure caused by SARS-CoV-2 lung damage, with the development of severe acute diffuse alveolar damage and cell-mediated immune response and myocardial involvement affected by SARS-CoV-2 damage. In this article, the authors introduce a clinical case of a child who dead from inflammatory myocardities with COVID-19 in a background of congenital heart disease and T-cell immunodeficiency.
Keywords: COVID-19; Myocarditis; SARS-CoV-2; cardiovascular inflammation; children; coronavirus infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
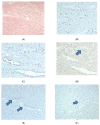
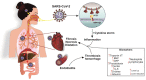
Similar articles
-
Cardiac Involvement in a Patient With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19).JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Jul 1;5(7):819-824. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1096. JAMA Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32219357 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Cardiac Involvement in Young Competitive Athletes.Circulation. 2021 Jul 27;144(4):256-266. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.054824. Epub 2021 Apr 17. Circulation. 2021. PMID: 33866822 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 and cardiac injury: clinical manifestations, biomarkers, mechanisms, diagnosis, treatment, and follow up.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2021 Mar;19(3):345-357. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2020.1822737. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2021. PMID: 32921216 Review.
-
Reversible Myocardial Injury Associated With SARS-CoV-2 in an Infant.JACC Case Rep. 2020 Dec;2(15):2348-2352. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2020.09.031. Epub 2020 Oct 12. JACC Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 33073245 Free PMC article.
-
Clinically Suspected Myocarditis in the Course of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Novel Coronavirus-2 Infection: Fact or Fiction?J Card Fail. 2021 Jan;27(1):92-96. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2020.11.002. Epub 2020 Nov 6. J Card Fail. 2021. PMID: 33166657 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High Risk of Heart Tumors after COVID-19.Life (Basel). 2023 Oct 20;13(10):2087. doi: 10.3390/life13102087. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895467 Free PMC article.
-
Features of Myocarditis: Morphological Differential Diagnosis in Post-COVID-19 Children.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jul 27;13(15):2499. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13152499. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morphological Changes in the Myocardium of Patients with Post-Acute Coronavirus Syndrome: A Study of Endomyocardial Biopsies.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jun 29;13(13):2212. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13132212. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37443606 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Chest Monitoring through Magnetic Resonance Angiogram Image Contrast Enhancement.Life (Basel). 2023 Nov 3;13(11):2160. doi: 10.3390/life13112160. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang L., Berger N.A., Kaelber D.C., Pamela B., Davis P.B., Volkow N.D., Xu R. Comparison of outcomes from COVID infection in pediatric and adult patients before and after the emergence of Omicron. medRxiv. 2022 doi: 10.1101/2021.12.30.21268495. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

