GAR-Net: Guided Attention Residual Network for Polyp Segmentation from Colonoscopy Video Frames
- PMID: 36611415
- PMCID: PMC9818392
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13010123
GAR-Net: Guided Attention Residual Network for Polyp Segmentation from Colonoscopy Video Frames
Erratum in
-
Correction: Raymann, J.; Rajalakshmi, R. GAR-Net: Guided Attention Residual Network for Polyp Segmentation from Colonoscopy Video Frames. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 123.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Apr 25;14(9):900. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14090900. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38732383 Free PMC article.
Abstract
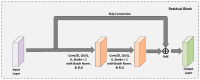
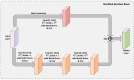
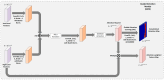
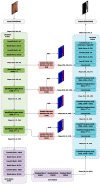
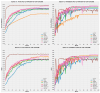
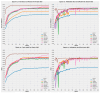
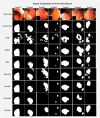
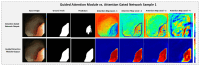
Colorectal Cancer is one of the most common cancers found in human beings, and polyps are the predecessor of this cancer. Accurate Computer-Aided polyp detection and segmentation system can help endoscopists to detect abnormal tissues and polyps during colonoscopy examination, thereby reducing the chance of polyps growing into cancer. Many of the existing techniques fail to delineate the polyps accurately and produce a noisy/broken output map if the shape and size of the polyp are irregular or small. We propose an end-to-end pixel-wise polyp segmentation model named Guided Attention Residual Network (GAR-Net) by combining the power of both residual blocks and attention mechanisms to obtain a refined continuous segmentation map. An enhanced Residual Block is proposed that suppresses the noise and captures low-level feature maps, thereby facilitating information flow for a more accurate semantic segmentation. We propose a special learning technique with a novel attention mechanism called Guided Attention Learning that can capture the refined attention maps both in earlier and deeper layers regardless of the size and shape of the polyp. To study the effectiveness of the proposed GAR-Net, various experiments were carried out on two benchmark collections viz., CVC-ClinicDB (CVC-612) and Kvasir-SEG dataset. From the experimental evaluations, it is shown that GAR-Net outperforms other previously proposed models such as FCN8, SegNet, U-Net, U-Net with Gated Attention, ResUNet, and DeepLabv3. Our proposed model achieves 91% Dice co-efficient and 83.12% mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) on the benchmark CVC-ClinicDB (CVC-612) dataset and 89.15% dice co-efficient and 81.58% mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) on the Kvasir-SEG dataset. The proposed GAR-Net model provides a robust solution for polyp segmentation from colonoscopy video frames.
Keywords: attention mechanism; colonoscopy; deep learning; healthcare informatics; medical image analysis; polyp segmentation; semantic segmentation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

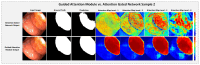
References
-
- Lawton C. Colonoscopic Polypectomy and Long-Term Prevention of Colorectal-Cancer Deaths. Yearb. Oncol. 2013;2013:128–129. doi: 10.1016/j.yonc.2013.04.004. - DOI
-
- Breier M., Gross S., Behrens A., Stehle T., Aach T. Active contours for localizing polyps in colonoscopic NBI image data. Med. Imaging 2011 Comput.-Aided Diagn. 2011;7963:79632M. doi: 10.1117/12.877986. - DOI
-
- Bernal J., Sánchez J., Vilariño F. Towards automatic polyp detection with a polyp appearance model. Pattern Recognit. 2012;45:3166–3182. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2012.03.002. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

