Prognostic Role of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Correlation with Oxidative Stress Markers in Locally Advanced and Metastatic Ovarian Cancer Patients
- PMID: 36611458
- PMCID: PMC9818969
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13010166
Prognostic Role of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Correlation with Oxidative Stress Markers in Locally Advanced and Metastatic Ovarian Cancer Patients
Abstract
Background: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) plays an important role in tumor progression in ovarian cancer, but the complex mechanism and interaction with oxidative stress are not fully understood.
Methods: A prospective study included 52 patients with ovarian adenocarcinoma stage IIIA-IV. Serum VEGF and reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as malondialdehyde and ceruloplasmin were measured.
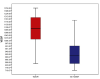
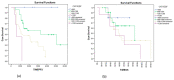
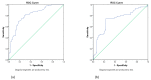
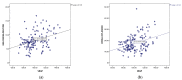
Results: VEGF levels were elevated (mean 1014.7 ± 165 pg/mL), especially in patients with macroscopic residual disease (1058 vs. 810 pg/mL, p = 0.0001). Median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were 6 and 40 months in patients with a very high VEGF (over 1200 pg/mL), 11 and 48 months in patients with VEGF between 1000-1200 pg/mL, 18 and 84 months in patients with VEGF between 800-1000 pg/mL, and not reached in patients with normal VEGF. Increased VEGF values were associated with a 2.6-fold increased risk of disease progression (HR = 2.60, 95% CI 1.69-3.99), and a 1.4-fold increased risk of death (HR = 1.4, 95% CI 1.15-1.91, p = 0.002). Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curves were used to validate VEGF as a prognostic factor and the area under the curve (AUC) was 0.814, p = 0.036 for PFS and 0.729, p = 0.043, for OS. There was a positive correlation between VEGF and malondialdehyde, Pearson coefficient of 0.35, p = 0.0001.
Conclusions: VEGF and malondialdehyde are important prognostic markers in ovarian cancer, especially in macroscopic residual disease, and there is a positive correlation between angiogenesis and oxidative stress.
Keywords: malondialdehyde; ovarian adenocarcinoma; vascular endothelial growth factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hanahan D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:31–46. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1059. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Loizzi V., Del Vecchio V., Gargano G., De Liso M., Kardashi A., Naglieri E., Resta L., Cicinelli E., Cormio G. Biological Pathways Involved in Tumor Angiogenesis and Bevacizumab Based Anti-Angiogenic Therapy with Special References to Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017;18:1967. doi: 10.3390/ijms18091967. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

