What Is Known about Midazolam? A Bibliometric Approach of the Literature
- PMID: 36611556
- PMCID: PMC9819597
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare11010096
What Is Known about Midazolam? A Bibliometric Approach of the Literature
Abstract
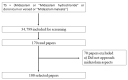
Midazolam is a drug with actions towards the central nervous system producing sedative and anticonvulsants effects, used for sedation and seizures treatments. A better understanding about its effects in the different scenarios presented in the literature could be helpful to gather information regarding its clinical indications, pharmacological interactions, and adverse events. From this perspective, the aim of this study was to analyze the global research about midazolam mapping, specifically the knowledge of the 100 most-cited papers about this research field. For this, a search was executed on the Web of Science-Core Collection database using bibliometric methodological tools. The search strategy retrieved 34,799 articles. A total of 170 articles were evaluated, with 70 articles being excluded for not meeting the inclusion criteria. The 100 most-cited articles rendered 42,480 citations on WoS-CC, ranging from 253 to 1744. Non-systematic review was the most published study type, mainly from North America, during the period of 1992 to 2002. The most frequent keywords were midazolam and pharmacokinetics. Regarding the authors, Thummel and Kunze were the ones with the greatest number of papers included. Our findings showed the global research trends about midazolam, mainly related to its different effects and uses throughout the time.
Keywords: bibliometrics; midazolam; sedation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Tomlin S. Medicines tailored for children—The introduction of buccal midazolam. Pharm. J. 2011;287:161–162.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

