Effect of Combined Exercise Program on Lower Extremity Alignment and Knee Pain in Patients with Genu Varum
- PMID: 36611582
- PMCID: PMC9819428
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare11010122
Effect of Combined Exercise Program on Lower Extremity Alignment and Knee Pain in Patients with Genu Varum
Abstract
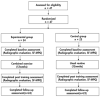
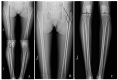
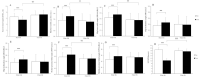
This study aimed to assess the effect of a combined exercise program on lower-extremity alignment and knee pain in patients with genu varum. Forty-seven middle-aged women with knee pain and genu varum were randomly divided into the exercise (EG, n = 24) and control (CG, n = 23) groups. The exercise group underwent a combined exercise program lasting 60 min in one session, three times a week for 12 weeks. Knee-to-knee length (KTKL), hip-knee-ankle angle (HKAA), hip inclination angle (HIA), and medial proximal tibial angle (MPTA) were assessed to evaluate lower-extremity alignment. To evaluate knee pain, the short form-McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ) were used. There was a significant difference between the groups, and a decrease of 16% in KTKL (from 6.48 ± 1.26 cm to 5.47 ± 1.21 cm) was shown in EG. Other variables, including HKAA, HIA, and MPTA on the right side, showed significant differences between pre- and post-intervention in EG (p < 0.01, p < 0.01, and p < 0.01, respectively). SF-MPQ score improved with 45% from 18.75 ± 1.64 to 10.33 ± 2.47 after exercise intervention in EG. These results suggest that the combined exercise program, including strength and neuromuscular exercises, is an effective intervention for improving lower-extremity alignment and knee pain in middle-aged women with genu varum.
Keywords: combined exercise; genu varum; hip inclination angle; hip–knee–ankle angle; knee pain; knee to knee length; lower extremity; middle-aged women.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biomechanical and Functional Improvements Gained by Proximal Tibia Osteotomy Correction of Genu Varum in Patients with Knee Pain.HSS J. 2020 Feb;16(1):30-38. doi: 10.1007/s11420-019-09670-6. Epub 2019 Mar 19. HSS J. 2020. PMID: 32015738 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of the lower limb components on genu varum in football players: a full leg length magnetic resonance imaging study.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025 Feb 25;17(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s13102-025-01075-9. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 40001230 Free PMC article.
-
Aggravation of Ankle Varus Incongruency Following Total Knee Replacement Correcting ≥10° of Genu Varum Deformity: A Radiographic Assessment.J Arthroplasty. 2020 Nov;35(11):3305-3310. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2020.06.027. Epub 2020 Jun 17. J Arthroplasty. 2020. PMID: 32646678
-
Change in the weight-bearing line ratio of the ankle joint and ankle joint line orientation after knee arthroplasty and high tibial osteotomy in patients with genu varum deformity.Int Orthop. 2021 Jan;45(1):117-124. doi: 10.1007/s00264-020-04799-0. Epub 2020 Sep 25. Int Orthop. 2021. PMID: 32975681
-
Femur originated genu varum in a patient with symptomatic ACL deficiency: a case report and review of literature.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 May 13;22(1):437. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04274-w. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021. PMID: 33985470 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The PLANS model predicts recurrent strokes in patients with minor ischemic strokes.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 17;15(1):9187. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93741-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40097644 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Lateral Wedge Insole With and Without Thigh and Abdominal Muscle Strengthening Exercises on the Balance of Young People With Genuvarum: A Randomize Controlled Trial.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 18;8(3):e70509. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70509. eCollection 2025 Mar. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40109698 Free PMC article.
-
Postoperative functional training program for vascularised Iliac flap donor site in jaw defect reconstruction based on the Delphi method.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 2;15(1):28224. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13774-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40753339 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Functional Recovery in a Patient of Abnormal Left Parieto-Occipital Encephalomalacia With Gliosis-Associated Genu Varum Deformity: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Feb 28;16(2):e55115. doi: 10.7759/cureus.55115. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38558677 Free PMC article.
-
High Expression Level of TRIP6 is Correlated with Poor Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer and Promotes Tumor Cell Proliferation and Migration.Biochem Genet. 2025 Feb;63(1):261-280. doi: 10.1007/s10528-024-10711-x. Epub 2024 Mar 2. Biochem Genet. 2025. PMID: 38430448
References
-
- Kendall F.P., McCreary E.K., Provance P.G., Rodgers M.M., Romani W. Muscles: Testing and Function, with Posture and Pain. 4th ed. Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2005. pp. 94–98.
-
- Howell S.M., Hull M.L. Kinematic alignment in total knee arthroplasty. In: Scott W.N., Insall J.N., editors. Insall & Scott Surgery of the Knee. 5th ed. Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2012. pp. 1255–1268.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

