The Effect of Early Neurological Stimulation on Puppy Welfare in Commercial Breeding Kennels
- PMID: 36611681
- PMCID: PMC9818019
- DOI: 10.3390/ani13010071
The Effect of Early Neurological Stimulation on Puppy Welfare in Commercial Breeding Kennels
Abstract
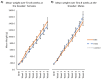
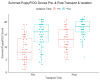
Throughout their lives, dogs may experience various stressful events. Early neurological stimulation (ENS), which was shown to alter stress responses beneficially in some animals, has not been fully explored in dogs. Seventy-six small-breed puppies from one commercial breeding kennel were divided into three treatment groups: ENS, held, and control. Puppies in the ENS group received 30 s of handling exercises for 21 days after birth; puppies in the held group were simply held for the same amount of time. Puppies in the control group were managed as per normal breeder practices (i.e., routine husbandry and physical health checks). Physical health was assessed weekly, and puppies were generally healthy and clean. Behavioral responses to stranger approach and isolation tests were evaluated pre- and post-ground-transportation to a distributor. Puppies were more affiliative toward a stranger post-isolation than pre-isolation (p < 0.001), and post-transport than pre-transport (p < 0.001). At the distributor, puppies in the isolation test spent less time in exploratory locomotion (p < 0.001) and vocalized more than at the breeder’s kennel (p = 0.011). Treatment did not affect these results. Overall, the results suggest that the type of ENS used in this study may not provide the purported benefits to puppies’ stress responses in commercial breeding populations.
Keywords: ENS; breeding dogs; canine welfare; early gentling; ground transportation; puppy development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Taylor K., Mills D. The Effect of the Kennel Environment on Canine Welfare: A Critical Review of Experimental Studies. Anim. Welfare. 2007;16:435–447.
-
- Moberg G.P. Biological Response to Stress: Implications for Animal Welfare. In: Moberg G.P., Mench J.A., editors. The Biology of Animal Stress: Basic Principles and Implications for Animal Welfare. CABI Publishing; Wallingford, UK: 2000. pp. 1–21.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

