Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 36611880
- PMCID: PMC9818928
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12010088
Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
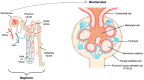
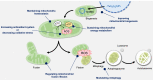
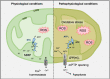
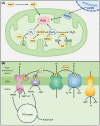
The kidney contains many mitochondria that generate ATP to provide energy for cellular processes. Oxidative stress injury can be caused by impaired mitochondria with excessive levels of reactive oxygen species. Accumulating evidence has indicated a relationship between oxidative stress and kidney diseases, and revealed new insights into mitochondria-targeted therapeutics for renal injury. Improving mitochondrial homeostasis, increasing mitochondrial biogenesis, and balancing mitochondrial turnover has the potential to protect renal function against oxidative stress. Although there are some reviews that addressed this issue, the articles summarizing the relationship between mitochondria-targeted effects and the risk factors of renal failure are still few. In this review, we integrate recent studies on oxidative stress and mitochondrial function in kidney diseases, especially chronic kidney disease. We organized the causes and risk factors of oxidative stress in the kidneys based in their mitochondria-targeted effects. This review also listed the possible candidates for clinical therapeutics of kidney diseases by modulating mitochondrial function.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; mitochondrial homeostasis; mitochondrial turnover; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wang Z.M., Yang Z.L., Bosy-westphal A., Zhang J.Y., Schautz B., Later W., Heymsfield S.B., Muller M.J. Specific meta-bolic rates of major organs and tissues across adulthood: Evaluation by mechanistic model of resting energy expenditure. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010;92:1369–1377. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2010.29885. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fredericks W.J., Yin H., Lal P., Puthiyaveettil R., Malkowicz S.B., Fredericks N.J., Tomaszewski J., Rauscher F.J., 3rd, Malkowicz S.B. Ectopic expression of the TERE1 (UBIAD1) protein inhibits growth of renal clear cell carcinoma cells: Altered metabolic phenotype associated with reactive oxygen species, nitric oxide and SXR target genes involved in cholesterol and lipid metabolism. Int. J. Oncol. 2013;43:638–652. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.1985. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

