Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Specialized Proresolving Lipid Mediators on Mesenchymal Stem Cells: An In Vitro Study
- PMID: 36611915
- PMCID: PMC9818697
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12010122
Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Specialized Proresolving Lipid Mediators on Mesenchymal Stem Cells: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
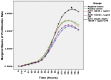
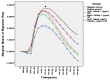
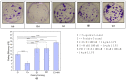
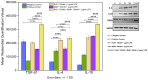
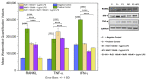
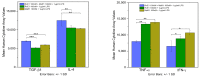
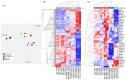
An interconnection between tissue inflammation and regeneration has been established through the regulation of defense and repair mechanisms within diseased dental tissue triggered by the release of immune-resolvent mediators. To better our understanding of the role of specific pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) in inflamed human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hBMMSCs), we studied the effects of Resolvin E1 (RvE1) and Maresin 1 (MaR1) in lipopoly-saccharide (LPS) stimulated hBMMSCs. The hBMMSCs were divided into five different groups, each of which was treated with or without SPMs. Group-1: negative control (no LPS stimulation), Group-2: positive control (LPS-stimulated), Group-3: RvE1 100 nM + 1 μg/mL LPS, Group-4: MaR1 100 nM + 1 µg/mL LPS, and Group-5: RvE1 100 nM + MaR1100 nM + 1 μg/mL LPS. Cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, colony formation, Western blotting, cytokine array, and LC/MS analysis were all performed on each group to determine the impact of SPMs on inflammatory stem cells. According to our data, RvE1 plus MaR1 effectively reduced inflammation in hBMMSCs. In particular, IL-4, 1L-10, and TGF-β1 activation and downregulation of RANKL, TNF-α, and IFN-γ compared to groups receiving single SPM were shown to be significantly different (Group 3 and 4). In addition, the LC/MS analysis revealed the differentially regulated peptide's role in immunological pathways that define the cellular state against inflammation. Inflamed hBMMSCs treated with a combination of Resolvin E1 (RvE1) and Maresin 1 (MaR1) promoted the highest inflammatory resolution compared to the other groups; this finding suggests a potential new approach of treating bacterially induced dental infections.
Keywords: LPS; Maresin1; Resolvin E1; SPMs; hBMMSCs; inflammation; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Impact of Resolvin-E1 and Maresin-1 on Bone Marrow Stem Cell Osteogenesis under Inflammatory Stress.Cells. 2024 May 28;13(11):932. doi: 10.3390/cells13110932. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38891064 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators on Craniofacial and Alveolar Bone Regeneration: Scoping Review.Braz Dent J. 2024 Oct 25;35:e246133. doi: 10.1590/0103-6440202406133. eCollection 2024. Braz Dent J. 2024. PMID: 39476116 Free PMC article.
-
Maresin-1 and Resolvin E1 Promote Regenerative Properties of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells Under Inflammatory Conditions.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 25;11:585530. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.585530. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33101318 Free PMC article.
-
Resolvin E1 accelerates pulp repair by regulating inflammation and stimulating dentin regeneration in dental pulp stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Jan 22;12(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02141-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33482900 Free PMC article.
-
Metabololipidomic profiling of functional immunoresolvent clusters and eicosanoids in mammalian tissues.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Oct 7;504(3):553-561. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.037. Epub 2018 Mar 15. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29524409 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel lipid mediator 7S,14R-docosahexaenoic acid: biogenesis and harnessing mesenchymal stem cells to ameliorate diabetic mellitus and retinal pericyte loss.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Mar 12;12:1380059. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1380059. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38533089 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Resolvin-E1 and Maresin-1 on Bone Marrow Stem Cell Osteogenesis under Inflammatory Stress.Cells. 2024 May 28;13(11):932. doi: 10.3390/cells13110932. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38891064 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators on Craniofacial and Alveolar Bone Regeneration: Scoping Review.Braz Dent J. 2024 Oct 25;35:e246133. doi: 10.1590/0103-6440202406133. eCollection 2024. Braz Dent J. 2024. PMID: 39476116 Free PMC article.
-
Fluconazole-Induced Protein Changes in Osteogenic and Immune Metabolic Pathways of Dental Pulp Mesenchymal Stem Cells of Osteopetrosis Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 8;24(18):13841. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813841. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762144 Free PMC article.
-
Low-dose pro-resolving mediators temporally reset the resolution response to microbial inflammation.Mol Med. 2024 Sep 18;30(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00877-w. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39294573 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

