Pharmacotherapy Evolution in Alzheimer's Disease: Current Framework and Relevant Directions
- PMID: 36611925
- PMCID: PMC9818415
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12010131
Pharmacotherapy Evolution in Alzheimer's Disease: Current Framework and Relevant Directions
Abstract
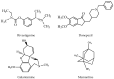
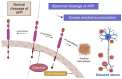
Alzheimer's disease (AD), once considered a rare disease, is now the most common form of dementia in the elderly population. Current drugs (cholinesterase inhibitors and glutamate antagonists) are safe but of limited benefit to most patients, offering symptomatic relief without successful cure of the disease. Since the last several decades, there has been a great need for the development of a treatment that might cure the underlying causes of AD and thereby slow its progression in vulnerable individuals. That is why phase I, II, and III studies that act on several fronts, such as cognitive improvement, symptom reduction, and enhancing the basic biology of AD, are imperative to stop the disease. This review discusses current treatment strategies, summarizing the clinical features and pharmacological properties, along with molecular docking analyses of the existing medications.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; cholinesterase inhibitors; cognitive improvement; glutamate antagonists; symptom reduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Alzheimer’s Disease. [(accessed on 26 May 2022)]. Available online: https://www.alzheimers.org.uk/about-dementia/types-dementia/alzheimers-d....
-
- Basics of Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia What Is Alzheimer’s Disease? [(accessed on 27 May 2022)]; Available online: https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/what-alzheimers-disease.
-
- Ritchie C., Smailagic N., Noel-Storr A.H., Ukoumunne O., Ladds E.C., Martin S. CSF tau and the CSF tau/ABeta ratio for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017;3:CD010803. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010803.pub2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

