Arf-like Protein 2 (ARL2) Controls Microtubule Neogenesis during Early Postnatal Photoreceptor Development
- PMID: 36611941
- PMCID: PMC9818799
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12010147
Arf-like Protein 2 (ARL2) Controls Microtubule Neogenesis during Early Postnatal Photoreceptor Development
Abstract
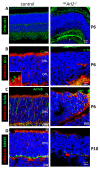
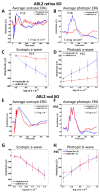
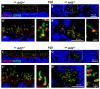
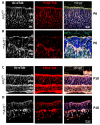
Arf-like protein 2 (ARL2) is a ubiquitously expressed small GTPase with multiple functions. In a cell culture, ARL2 participates with tubulin cofactor D (TBCD) in the neogenesis of tubulin αβ-heterodimers, the building blocks of microtubules. To evaluate this function in the retina, we conditionally deleted ARL2 in mouse retina at two distinct stages, either during the embryonic development (retArl2-/-) or after ciliogenesis specifically in rods (rodArl2-/-). retArl2-/- retina sections displayed distorted nuclear layers and a disrupted microtubule cytoskeleton (MTC) as early as postnatal day 6 (P6). Rod and cone outer segments (OS) did not form. By contrast, the rod ARL2 knockouts were stable at postnatal day 35 and revealed normal ERG responses. Cytoplasmic dynein is reduced in retArl2-/- inner segments (IS), suggesting that dynein may be unstable in the absence of a normal MTC. We investigated the microtubular stability in the absence of either ARL2 (retARL2-/-) or DYNC1H1 (retDync1h1-/-), the dynein heavy chain, and found that both the retArl2-/- and retDync1h1-/- retinas exhibited reduced microtubules and nuclear layer distortion. The results suggest that ARL2 and dynein depend on each other to generate a functional MTC during the early photoreceptor development.
Keywords: Arf-like protein 2 (ARL2); dynein heavy chain (DYNC1H1); microtubule cytoskeleton (MTC); retina; rod photoreceptors; tubulin αβ-heterodimers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Trimer Consisting of the Tubulin-specific Chaperone D (TBCD), Regulatory GTPase ARL2, and β-Tubulin Is Required for Maintaining the Microtubule Network.J Biol Chem. 2017 Mar 10;292(10):4336-4349. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.770909. Epub 2017 Jan 26. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28126905 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of a zebrafish dync1h1 mutant reveals multiple functions for cytoplasmic dynein 1 during retinal photoreceptor development.Neural Dev. 2010 Apr 22;5:12. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-5-12. Neural Dev. 2010. PMID: 20412557 Free PMC article.
-
Tubulin cofactors and Arl2 are cage-like chaperones that regulate the soluble αβ-tubulin pool for microtubule dynamics.Elife. 2015 Jul 24;4:e08811. doi: 10.7554/eLife.08811. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26208336 Free PMC article.
-
Higher order signaling: ARL2 as regulator of both mitochondrial fusion and microtubule dynamics allows integration of 2 essential cell functions.Small GTPases. 2016 Oct;7(4):188-196. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1211069. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Small GTPases. 2016. PMID: 27400436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review: Cytoplasmic dynein motors in photoreceptors.Mol Vis. 2021 Sep 1;27:506-517. eCollection 2021. Mol Vis. 2021. PMID: 34526758 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Arl2 GTPase associates with the centrosomal protein Cdk5rap2 to regulate cortical development via microtubule organization.PLoS Biol. 2024 Aug 13;22(8):e3002751. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002751. eCollection 2024 Aug. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 39137170 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Dync1h1 on Phototransduction Protein Transport and the Development and Maintenance of Photoreceptor Cells in Zebrafish.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 Feb 3;66(2):38. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.2.38. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 39946138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cavenagh M.M., Breiner M., Schurmann A., Rosenwald A.G., Terui T., Zhang C., Randazzo P.A., Adams M., Joost H.G., Kahn R.A. ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF)-like 3, a new member of the ARF family of GTP-binding proteins cloned from human and rat tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:18937–18942. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(17)32257-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schurmann A., Breiner M., Becker W., Huppertz C., Kainulainen H., Kentrup H., Joost H.G. Cloning of two novel ADP-ribosylation factor-like proteins and characterization of their differential expression in 3T3-L1 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:15683–15688. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(17)40735-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

