Exosome-Derived microRNA: Implications in Melanoma Progression, Diagnosis and Treatment
- PMID: 36612077
- PMCID: PMC9818028
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15010080
Exosome-Derived microRNA: Implications in Melanoma Progression, Diagnosis and Treatment
Abstract
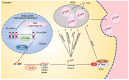
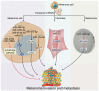
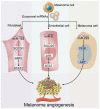
Melanoma is a malignant and aggressive cancer, and its progression is greatly affected by interactions between melanoma cells and their surroundings. Exploration on mechanism of melanoma and improved diagnostic and therapeutic strategies are becoming increasingly important. Unlike extracellular messengers that mainly work on targeted cells through corresponding receptors, exosomes are essential intercellular messengers that deliver biologically active substances such as nucleic acids and proteins to target cells for cell-cell communication. Of them, microRNAs (miRNAs) are common and important exosomal components that can regulate the expression of a wide range of target genes. Accordingly, exosome-derived miRNAs play a significant role in melanoma progression, including invasion and metastasis, microenvironment establishment, angiogenesis, and immune escape. MiRNA signatures of exosomes are specific in melanoma patients compared to healthy controls, thus circulating miRNAs, especially exosomal miRNAs, become potential diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets for melanoma. This review aims to summarize recent studies on the role of exosomal miRNAs in melanoma as well as ongoing efforts in melanoma treatment.
Keywords: diagnosis; exosome; melanoma; microRNA; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MiRNA in melanoma-derived exosomes.Cancer Lett. 2014 May 28;347(1):29-37. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.02.004. Epub 2014 Feb 7. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 24513178
-
Exosomal microRNAs in lung cancer: a narrative review.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 30;13(6):3090-3105. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-2319. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38988916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Exosome-Derived microRNA on Lung Cancer Metastasis Progression.Biomolecules. 2023 Oct 25;13(11):1574. doi: 10.3390/biom13111574. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38002256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxic BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs promote metastasis of lung cancer cells via STAT3-induced EMT.Mol Cancer. 2019 Mar 13;18(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-0959-5. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30866952 Free PMC article.
-
Expression, regulation, and function of exosome-derived miRNAs in cancer progression and therapy.FASEB J. 2021 Oct;35(10):e21916. doi: 10.1096/fj.202100294RR. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 34510546 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Culture Duration on the Properties and Functionality of Yeast-Derived Extracellular Vesicles.Biomater Res. 2025 May 6;29:0201. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0201. eCollection 2025. Biomater Res. 2025. PMID: 40330275 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression in tumor and adjacent normal tissues in lung adenocarcinoma subtypes.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 14;25(1):1169. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14496-z. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40660181 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological and Therapeutic Significance of Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer Cell Migration and Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Sep 5;15(18):4425. doi: 10.3390/cancers15184425. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SOX10, MITF, and microRNAs: Decoding their interplay in regulating melanoma plasticity.Int J Cancer. 2025 Oct 1;157(7):1277-1293. doi: 10.1002/ijc.35499. Epub 2025 Jun 3. Int J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40458894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cutaneous Melanoma: A Review of Multifactorial Pathogenesis, Immunohistochemistry, and Emerging Biomarkers for Early Detection and Management.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 1;24(21):15881. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115881. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958863 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

