Adherence to the CDK 4/6 Inhibitor Palbociclib and Omission of Dose Management Supported by Pharmacometric Modelling as Part of the OpTAT Study
- PMID: 36612312
- PMCID: PMC9818079
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15010316
Adherence to the CDK 4/6 Inhibitor Palbociclib and Omission of Dose Management Supported by Pharmacometric Modelling as Part of the OpTAT Study
Abstract
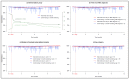
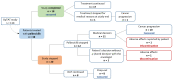
The cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor (CDK4/6i) palbociclib is administered orally and cyclically, causing medication adherence challenges. We evaluated components of adherence to palbociclib, its relationship with pharmacokinetics (PK), and drug-induced neutropenia. Patients with metastatic breast cancer (MBC) receiving palbociclib, delivered in electronic monitors (EM), were randomized 1:1 to an intervention and a control group. The intervention was a 12-month interprofessional medication adherence program (IMAP) along with monthly motivational interviews by a pharmacist. Implementation adherence was compared between groups using generalized estimating equation models, in which covariates were included. Model-based palbociclib PK and neutrophil profiles were simulated under real-life implementation scenarios: (1) optimal, (2) 2 doses omitted and caught up at cycle end. At 6 months, implementation was slightly higher and more stable in the intervention (n = 19) than in the control (n = 19) group, 99.2% and 97.3% (Δ1.95%, 95% CI 1.1−2.9%), respectively. The impact of the intervention was larger in patients diagnosed with MBC for >2 years (Δ3.6%, 95% CI 2.1−5.4%), patients who received >4 cycles before inclusion (Δ3.1%, 95% CI 1.7−4.8%) and patients >65 (Δ2.3%, 95% CI 0.8−3.6%). Simulations showed that 25% of patients had neutropenia grade ≥3 during the next cycle in scenario 1 versus 30% in scenario 2. Education and monitoring of patient CDK4/6i cycle management and adherence along with therapeutic drug monitoring can help clinicians improve prescription and decrease toxicity.
Keywords: CDK4/6 inhibitor; electronic adherence monitoring; interprofessionality; medication adherence; motivational interviewing; neutropenia; oral anticancer therapy; palbociclib; pharmacists.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A pharmacist-led interprofessional medication adherence program improved adherence to oral anticancer therapies: The OpTAT randomized controlled trial.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 7;19(6):e0304573. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304573. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38848380 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Optimizing Oral Targeted Anticancer Therapies Study for Patients With Solid Cancer: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Medication Adherence Program Along With Systematic Collection and Modeling of Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Data.JMIR Res Protoc. 2021 Jun 29;10(6):e30090. doi: 10.2196/30090. JMIR Res Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34185020 Free PMC article.
-
The differential impact of a 6-versus 12-month pharmacist-led interprofessional medication adherence program on medication adherence in patients with diabetic kidney disease: the randomized PANDIA-IRIS study.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 24;15:1294436. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1294436. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38327981 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Management of Potential Toxicities and Drug Interactions Related to Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitors in Breast Cancer: Practical Considerations and Recommendations.Oncologist. 2017 Sep;22(9):1039-1048. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0142. Epub 2017 Jul 13. Oncologist. 2017. PMID: 28706010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CDK4/6 Inhibitors Expand the Therapeutic Options in Breast Cancer: Palbociclib, Ribociclib and Abemaciclib.BioDrugs. 2019 Apr;33(2):125-135. doi: 10.1007/s40259-019-00337-6. BioDrugs. 2019. PMID: 30847853 Review.
Cited by
-
Real-World Analysis of Adherence to Abemaciclib and Endocrine Therapy in Women with HR+/HER2- Breast Cancer.Biomedicines. 2025 Feb 21;13(3):546. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13030546. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40149523 Free PMC article.
-
A pharmacist-led interprofessional medication adherence program improved adherence to oral anticancer therapies: The OpTAT randomized controlled trial.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 7;19(6):e0304573. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304573. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38848380 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Real-world pharmacokinetics of trametinib in pediatric low-grade glioma.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 25;95(1):35. doi: 10.1007/s00280-025-04761-0. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39998657
-
Population Pharmacokinetics of Trametinib and Impact of Nonadherence on Drug Exposure in Oncology Patients as Part of the Optimizing Oral Targeted Anticancer Therapies Study.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jun 11;16(12):2193. doi: 10.3390/cancers16122193. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927898 Free PMC article.
-
Combined treatment with CDK4/6, CDK2, and CXCR1/2 inhibitors effectively halts the growth of BRAF wild-type melanoma tumors.Front Oncol. 2025 Aug 19;15:1609735. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1609735. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40904502 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ligue-Suisse-Contre-Le-Cancer Les Chiffres Du Cancer-Période Considérée: Années 2014 à 2018. [(accessed on 28 February 2022)]. Available online: https://www.liguecancer.ch/a-propos-du-cancer/les-chiffres-du-cancer/?gc....
-
- Caswell-Jin J.L., Sun L., Munoz D., Lu Y., Li Y., Huang H., Hampton J.M., Song J., Jayasekera J., Schechter C., et al. Contributions of screening, early-stage treatment, and metastatic treatment to breast cancer mortality reduction by molecular subtype in U.S. women, 2000–2017. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022;40:1008. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.1008. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

