Empowerment-Based Physical Activity Intervention for People with Advanced Dry Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Mixed-Methods Protocol
- PMID: 36612963
- PMCID: PMC9819966
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20010643
Empowerment-Based Physical Activity Intervention for People with Advanced Dry Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Mixed-Methods Protocol
Abstract
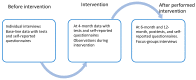
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the most common cause of incurable visual impairment and impacts daily life. These impacts include loss of social activities, decreased functional independence, and reduced physical activity. This protocol aims to describe a prospective, mixed-methodology for studying a population with AMD before, during, and after an empowerment-based physical activity intervention (EPI). A study framework was also developed for EPI. The intervention will include 20 older individuals (age 65+ years) with AMD recruited in Sweden. The intervention period is six months and comprises adapted physical activity and social activities in a group twice a week and individual health coaching on three occasions. The quantitative pre-test and three follow-ups include physical functional tests, an accelerometer that monitors physical activity continuously for one week, and questionnaires. Individual and focus-group interviews and ethnographic observations will explore the experience of living with AMD and what it means to participate in the EPI for individuals with AMD. The chosen methodology offers a structured way for researchers to explore the experiences and factors that may provide insights into the potential of creative supervised, adapted physical activity in groups, health coaching, and socialising that are significant to enable well-being among older individuals with AMD.
Keywords: adapted physical activity; age-related macular degeneration; empowerment; intervention; mixed methods.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
An Empowerment-Based Physical Activity Intervention for Older People with Advanced Age-Related Macular Degeneration: An Exploratory Qualitative Case Study Design.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 4;13(13):3918. doi: 10.3390/jcm13133918. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38999484 Free PMC article.
-
Perpetuating ability to live life as usual: a grounded theory study of persons living with age-related macular degeneration.BMC Geriatr. 2024 Jan 22;24(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-04689-9. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 38254006 Free PMC article.
-
Age related macular degeneration and visual disability.Curr Drug Targets. 2011 Feb;12(2):221-33. doi: 10.2174/138945011794182755. Curr Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 20887239
-
Global Burden of Dry Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Targeted Literature Review.Clin Ther. 2021 Oct;43(10):1792-1818. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2021.08.011. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Clin Ther. 2021. PMID: 34548176 Review.
-
Visual cycle modulators versus placebo or observation for the prevention and treatment of geographic atrophy due to age-related macular degeneration.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Dec 17;12(12):CD013154. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013154.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33331670 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
An Empowerment-Based Physical Activity Intervention for Older People with Advanced Age-Related Macular Degeneration: An Exploratory Qualitative Case Study Design.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 4;13(13):3918. doi: 10.3390/jcm13133918. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38999484 Free PMC article.
-
Perpetuating ability to live life as usual: a grounded theory study of persons living with age-related macular degeneration.BMC Geriatr. 2024 Jan 22;24(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-04689-9. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 38254006 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical