Lifestyle and Health-Related Quality of Life Relationships Concerning Metabolic Disease Phenotypes on the Nutrimdea Online Cohort
- PMID: 36613089
- PMCID: PMC9819172
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20010767
Lifestyle and Health-Related Quality of Life Relationships Concerning Metabolic Disease Phenotypes on the Nutrimdea Online Cohort
Abstract
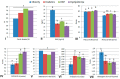
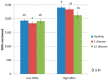
Obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular events are non-communicable diseases (NCDs) directly related to lifestyle and life quality. Rises on NCDs rates are leading to increases in early deaths concerning metabolic morbidities. Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) has been described as a subjective perception about the influence of health and personal features on human well-being. This study aimed to characterize phenotypic and lifestyle roles on the occurrence of metabolic diseases and determine the potential mutual interactions and with HRQoL. Data from an online adult population (NUTRiMDEA study, n = 17,332) were used to estimate an adapted Obesogenic Score (ObS), while logistic regression analyses were fitted in order to examine relevant factors related to the prevalence of different metabolic diseases including HRQoL. Sex and age showed significant differences depending on lifestyle and metabolic health (p < 0.05). Adherence to the Mediterranean diet and physical activity showed a mutual interaction concerning ObS (p < 0.001), as well with metabolic health (p = 0.044). Furthermore, metabolic diseases showed own features related to sociodemographic and lifestyle characteristics in this population. Metabolic syndrome components may be differently influenced by diverse lifestyle or socioeconomic factors which in turn affect the perceived HRQoL. These outcomes should be taken into account individually for a precision medicine and public health purposes.
Keywords: Mediterranean diet; health-related quality of life; metabolic health and disease; online data collection; physical activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bennett J.E., Stevens G.A., Mathers C.D., Bonita R., Rehm J., Kruk M.E., Riley L.M., Dain K., Kengne A.P., Chalkidou K., et al. NCD Countdown 2030: Worldwide trends in non-communicable disease mortality and progress towards Sustainable Development Goal target 3.4. Lancet. 2018;392:1072–1088. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31992-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization The Top 10 Causes of Death. [(accessed on 19 June 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death.
-
- Roth G.A., Abate D., Abate K.H., Abay S.M., Abbafati C., Abbasi N., Abbastabar H., Abd-Allah F., Abdela J., Abdelalim A., et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1736–1788. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32203-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Budreviciute A., Damiati S., Sabir D.K., Onder K., Schuller-Goetzburg P., Plakys G., Katileviciute A., Khoja S., Kodzius R. Management and Prevention Strategies for Non-communicable Diseases (NCDs) and Their Risk Factors. Front. Public Health. 2020;8:574111. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.574111. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

