The IL-1 Family and Its Role in Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 36613465
- PMCID: PMC9820551
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24010017
The IL-1 Family and Its Role in Atherosclerosis
Abstract
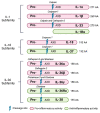
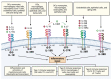
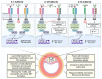
The IL-1 superfamily of cytokines is a central regulator of immunity and inflammation. The family is composed of 11 cytokines (with agonist, antagonist, and anti-inflammatory properties) and 10 receptors, all tightly regulated through decoy receptor, receptor antagonists, and signaling inhibitors. Inflammation not only is an important physiological response against infection and injury but also plays a central role in atherosclerosis development. Several clinical association studies along with experimental studies have implicated the IL-1 superfamily of cytokines and its receptors in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease. Here, we summarize the key features of the IL-1 family, its role in immunity and disease, and how it helps shape the development of atherosclerosis.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; cardiovascular disease; inflammation; interleukin-1 family.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dai H., Much A.A., Maor E., Asher E., Younis A., Xu Y., Lu Y., Liu X., Shu J., Bragazzi N.L. Global, regional, and national burden of ischaemic heart disease and its attributable risk factors, 1990–2017: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Eur. Heart J. Qual. Care Clin. Outcomes. 2022;8:50–60. doi: 10.1093/ehjqcco/qcaa076. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

