Lung Damage in Rheumatoid Arthritis-A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 36613472
- PMCID: PMC9820047
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24010028
Lung Damage in Rheumatoid Arthritis-A Retrospective Study
Abstract
The current study aimed to evaluate rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD) in clinical practice and whether disease characteristics are associated with X-ray and high-resolution computed tomography (HR-CT) findings. Medical history of RA patients from a tertiary rheumatology clinic was retrieved from its electronic database starting from 1 January 2019 until the study date (8 August 2022) using International Classification of Disease version 10 codes for RA, ILD and exclusion criteria. The study included 78 RA patients (75.6% women, 15.4% active smokers), with average time from RA to ILD of 5.6 years. Regarding chest X-ray findings, men had a higher prevalence of nodules, combined fibrosis and nodules and combined bronchiectasis and nodules, rheumatoid factor (RF)-positive patients had a higher prevalence of fibrosis and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies (ACPA)-positive patients had a higher prevalence of bronchiectasis. Regarding HR-CT findings, patients actively treated with methotrexate had a higher prevalence of nodules; a combination of fibrosis and nodules; combination of emphysema and nodules; and combination of fibrosis, emphysema and nodules. ILD develops within approximately 5 years from RA diagnosis, and ILD-associated imaging findings on chest X-rays and HR-CT are more prevalent among men with RA, among patients with positive RA serology (RF and/or ACPA) and RA patients on methotrexate.
Keywords: interstitial pulmonary fibrosis; pulmonary nodules; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
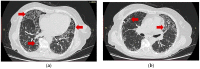
Figures

References
-
- Travis W.D., Costabel U., Hansell D.M., King T.E., Jr., Lynch D.A., Nicholson A.G., Ryerson C.J., Ryu J.H., Selman M., Wells A.U., et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013;188:733–748. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201308-1483ST. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Charles P.J., Sweatman M.C., Markwick J.R., Maini R.N. Maini. HLA-B40: A marker for susceptibility to lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Dis. Markers. 1991;9:97–101. - PubMed
-
- Hillarby M.C., McMahon M.J., Grennan D.M., Cooper R.G., Clarkson R.W.E., Davies E.J., Sanders P.A., Chatitopadhyay C., Swinson D. HLA associations in subjects with rheumatoid arthritis and bronchiectasis but not with other pulmonary complications of rheumatoid disease. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1993;32:794–797. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/32.9.794. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

