Prediction of Drug Synergism between Peptides and Antineoplastic Drugs Paclitaxel, 5-Fluorouracil, and Doxorubicin Using In Silico Approaches
- PMID: 36613510
- PMCID: PMC9820768
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24010069
Prediction of Drug Synergism between Peptides and Antineoplastic Drugs Paclitaxel, 5-Fluorouracil, and Doxorubicin Using In Silico Approaches
Abstract
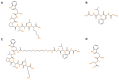
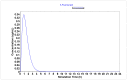
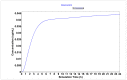
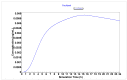
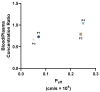
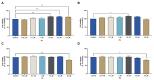
Chemotherapy is the main treatment for most early-stage cancers; nevertheless, its efficacy is usually limited by drug resistance, toxicity, and tumor heterogeneity. Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are small peptide sequences that can be used to increase the delivery rate of chemotherapeutic drugs to the tumor site, therefore contributing to overcoming these problems and enhancing the efficacy of chemotherapy. The drug combination is another promising strategy to overcome the aforementioned problems since the combined drugs can synergize through interconnected biological processes and target different pathways simultaneously. Here, we hypothesized that different peptides (P1-P4) could be used to enhance the delivery of chemotherapeutic agents into three different cancer cells (HT-29, MCF-7, and PC-3). In silico studies were performed to simulate the pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters of each peptide and antineoplastic agent to help predict synergistic interactions in vitro. These simulations predicted peptides P2-P4 to have higher bioavailability and lower Tmax, as well as the chemotherapeutic agent 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) to have enhanced permeability properties over other antineoplastic agents, with P3 having prominent accumulation in the colon. In vitro studies were then performed to evaluate the combination of each peptide with the chemotherapeutic agents as well as to assess the nature of drug interactions through the quantification of the Combination Index (CI). Our findings in MCF-7 and PC-3 cancer cells demonstrated that the combination of these peptides with paclitaxel (PTX) and doxorubicin (DOXO), respectively, is not advantageous over a single treatment with the chemotherapeutic agent. In the case of HT-29 colorectal cancer cells, the combination of P2-P4 with 5-FU resulted in synergistic cytotoxic effects, as predicted by the in silico simulations. Taken together, these findings demonstrate that these CPP6-conjugates can be used as adjuvant agents to increase the delivery of 5-FU into HT-29 colorectal cancer cells. Moreover, these results support the use of in silico approaches for the prediction of the interaction between drugs in combination therapy for cancer.
Keywords: cancer therapy; cell-penetrating peptides; drug combination; drug synergism; in silico.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Synergistic Interaction of CPP2 Coupled with Thiazole Derivates Combined with Clotrimazole and Antineoplastic Drugs in Prostate and Colon Cancer Cell Lines.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 5;22(21):11984. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111984. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769414 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Growth Inhibition of HT-29 Colon and MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells with Simultaneous and Sequential Combinations of Antineoplastics and CNS Drugs.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 10;22(14):7408. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147408. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299028 Free PMC article.
-
Roscovitine synergizes with conventional chemo-therapeutic drugs to induce efficient apoptosis of human colorectal cancer cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Sep 7;14(33):5162-75. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5162. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18777593 Free PMC article.
-
Paclitaxel combination therapy in the treatment of metastatic breast cancer: a review.Semin Oncol. 1996 Oct;23(5 Suppl 11):46-56. Semin Oncol. 1996. PMID: 8893900 Review.
-
The development of peptide-drug conjugates (PDCs) strategies for paclitaxel.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2022 Feb;19(2):147-161. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2022.2039621. Epub 2022 Feb 13. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35130795 Review.
Cited by
-
New Perspective for Using Antimicrobial and Cell-Penetrating Peptides to Increase Efficacy of Antineoplastic 5-FU in Cancer Cells.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Dec 12;14(12):565. doi: 10.3390/jfb14120565. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 38132819 Free PMC article.
-
The Beta2-adrenergic agonist salbutamol synergizes with paclitaxel on cell proliferation and tumor growth in triple negative breast cancer models.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2023 Dec;92(6):485-499. doi: 10.1007/s00280-023-04586-9. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37725114
-
Safety and Efficacy of Antiviral Drugs and Vaccines in Pregnant Women: Insights from Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Integration of Viral Infection Dynamics.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Jul 16;12(7):782. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12070782. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39066420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Small Sugar Molecule with Huge Potential in Targeted Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 11;15(3):913. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030913. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36986774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide-based drugs in immunotherapy: current advances and future prospects.Med Oncol. 2025 Apr 23;42(5):177. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02739-9. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40266466 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

