Magnesium and the Brain: A Focus on Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration
- PMID: 36613667
- PMCID: PMC9820677
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24010223
Magnesium and the Brain: A Focus on Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration
Abstract
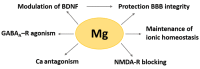
Magnesium (Mg) is involved in the regulation of metabolism and in the maintenance of the homeostasis of all the tissues, including the brain, where it harmonizes nerve signal transmission and preserves the integrity of the blood-brain barrier. Mg deficiency contributes to systemic low-grade inflammation, the common denominator of most diseases. In particular, neuroinflammation is the hallmark of neurodegenerative disorders. Starting from a rapid overview on the role of magnesium in the brain, this narrative review provides evidences linking the derangement of magnesium balance with multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's, and Parkinson's diseases.
Keywords: blood–brain barrier; brain; magnesium; neurodegeneration; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Poleszak E. Benzodiazepine/GABA(A) receptors are involved in magnesium-induced anxiolytic-like behavior in mice. Pharmacol. Rep. 2008;60:483–489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

