Galectin-2 in Health and Diseases
- PMID: 36613785
- PMCID: PMC9820181
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24010341
Galectin-2 in Health and Diseases
Abstract
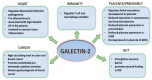
Galectin-2 is a prototype member of the galactoside-binding galectin family. It is predominately expressed in the gastrointestinal tract but is also detected in several other tissues such as the placenta and in the cardiovascular system. Galectin-2 expression and secretion by epithelial cells has been reported to contribute to the strength of the mucus layer, protect the integrity of epithelia. A number of studies have also suggested the involvement of galectin-2 in tissue inflammation, immune response and cell apoptosis. Alteration of galectin-2 expression occurs in inflammatory bowel disease, coronary artery diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, and pregnancy disorders and has been shown to be involved in disease pathogenesis. This review discusses our current understanding of the role and actions of galectin-2 in regulation of these pathophysiological conditions.
Keywords: apoptosis; galectin-2; gastrointestinal tract; immune cell; pregnancy disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

