Innovative Anti-CD38 and Anti-BCMA Targeted Therapies in Multiple Myeloma: Mechanisms of Action and Resistance
- PMID: 36614086
- PMCID: PMC9820921
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24010645
Innovative Anti-CD38 and Anti-BCMA Targeted Therapies in Multiple Myeloma: Mechanisms of Action and Resistance
Abstract
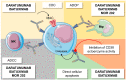
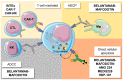
CD38 and B-cell maturation antigens (BCMAs) are prevalently expressed on neoplastic plasma cells in multiple myeloma (MM), making them ideal therapeutic targets. Anti-CD38 monoclonal antibodies, such as approved daratumumab and isatuximab, are currently the milestone in MM treatment because they induce plasma cell apoptosis and kill through several mechanisms, including antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity or phagocytosis. BCMA is considered an excellent target in MM, and three different therapeutic strategies are either already available in clinical practice or under investigation: antibody-drug conjugates, such as belantamab-mafodotin; bispecific T cell engagers; and chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cell therapies. Despite the impressive clinical efficacy of these new strategies in the treatment of newly diagnosed or multi-refractory MM patients, several mechanisms of resistance have already been described, including antigen downregulation, the impairment of antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity and phagocytosis, T- and natural killer cell senescence, and exhaustion. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge on the mechanisms of action and resistance of anti-CD38 and anti-BCMA agents and their clinical efficacy and safety.
Keywords: BCMA; CD38; anti-BCMA CAR-T; anti-BCMA bispecific antibodies; anti-CD38 antibodies; mechanisms of resistance; multiple myeloma; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dianzani U., Funaro A., DiFranco D., Garbarino G., Bragardo M., Redoglia V., Buonfiglio D., De Monte L.B., Pileri A., Malavasi F. Interaction between endothelium and CD4+CD45RA+ lymphocytes. Role of the human CD38 molecule. J. Immunol. 1994;153:952–959. - PubMed
-
- Deaglio S., Morra M., Mallone R., Ausiello C.M., Prager E., Garbarino G., Dianzani U., Stockinger H., Malavasi F. Human CD38 (ADP-ribosyl cyclase) is a counter-receptor of CD31, an Ig superfamily member. J. Immunol. 1998;160:395–402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

