Apoe4 and Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis-Mitochondrial Deregulation and Targeted Therapeutic Strategies
- PMID: 36614219
- PMCID: PMC9821307
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24010778
Apoe4 and Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis-Mitochondrial Deregulation and Targeted Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
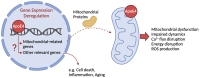
APOE ε4 allele (ApoE4) is the primary genetic risk factor for sporadic Alzheimer's disease (AD), expressed in 40-65% of all AD patients. ApoE4 has been associated to many pathological processes possibly linked to cognitive impairment, such as amyloid-β (Aβ) and tau pathologies. However, the exact mechanism underlying ApoE4 impact on AD progression is unclear, while no effective therapies are available for this highly debilitating neurodegenerative disorder. This review describes the current knowledge of ApoE4 interaction with mitochondria, causing mitochondrial dysfunction and neurotoxicity, associated with increased mitochondrial Ca2+ and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, and it effects on mitochondrial dynamics, namely fusion and fission, and mitophagy. Moreover, ApoE4 translocates to the nucleus, regulating the expression of genes involved in aging, Aβ production, inflammation and apoptosis, potentially linked to AD pathogenesis. Thus, novel therapeutical targets can be envisaged to counteract the effects induced by ApoE4 in AD brain.
Keywords: aging; dementia; gene expression; mitochondrial function; mitochondrial morphology; neuroinflammation; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Prince M., Wimo A., Guerchet M. World Alzheimer Report 2015, The Global Impact of Dementia: An Analysis of Prevalence, Incidence, Cost and Trends. Alzheimer’s Disease International; London, UK: 2015. pp. 6–27.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

