Diagnostic and Prognostic Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Pancreatic Cancer: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 36614326
- PMCID: PMC9821035
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24010885
Diagnostic and Prognostic Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Pancreatic Cancer: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives
Abstract
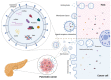
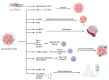
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most aggressive tumors, with a dismal prognosis due to poor detection rates at early stages, rapid progression, post-surgical complications, and limited effectiveness of conventional oncologic therapies. There are no consistently reliable biomarkers or imaging modalities to accurately diagnose, classify, and predict the biological behavior of this tumor. Therefore, it is imperative to develop new and improved strategies to detect pancreatic lesions in the early stages of cancerization with greater sensitivity and specificity. Extracellular vesicles, including exosome and microvesicles, are membrane-coated cellular products that are released in the outer environment. All cells produce extracellular vesicles; however, this process is enhanced by inflammation and tumorigenesis. Based on accumulating evidence, extracellular vesicles play a crucial role in pancreatic cancer progression and chemoresistance. Moreover, they may represent potential biomarkers and promising therapy targets. The aim of the present review is to review the current evidence on the role of extracellular vesicles in pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: biomarkers; early diagnosis; extracellular vesicles; liquid biopsy; microRNA; pancreatic cancer; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical