Characteristics of Patients Treated with JAK Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis before versus after VTE Risk Warnings
- PMID: 36615007
- PMCID: PMC9820905
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12010207
Characteristics of Patients Treated with JAK Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis before versus after VTE Risk Warnings
Abstract
Background: Baricitinib (BARI) or Tofacitinib (TOFA) were the first Janus Kinase Inhibitors (JAKi) to be marketed in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Concerns regarding venous thromboembolism (VTE) risk have emerged during the past years. The aim of the study was to compare the baseline characteristics of patients initiating BARI or TOFA in RA before versus after European Medicine Agency (EMA)'s VTE warnings and to compare real-world persistence with these two drugs.
Methods: In this multicentric cohort study, RA patients initiating BARI or TOFA were included from October 2017, date of BARI marketing authorization in France, to September 2020. Baseline characteristics regarding VTE risk were compared (before vs. after May 2019) by using pre-specified statistical tests. Comparison of persistence was assessed by using propensity-score methods.
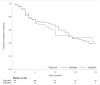
Results: 232 patients were included; 155 with BARI and 77 with TOFA. Baseline characteristics of patients regarding VTE risk factors were not statistically different when Janus Kinase inhibitor (JAKi) was initiated before vs. after EMA's warnings although a trend towards a lower proportion of VTE history was observed. Five VTE events occurred, four with BARI, one with TOFA. Cumulative persistence rate at 2 years was similar between BARI and TOFA: HR 0.96; 95% Cl: 0.52 to 1.74; p = 0.89.
Conclusions: Our study did not show a significant change in patients characteristics starting a JAKi after the EMA's warnings, probably due to a lack of power. Though, the lower proportion of VTE history in patients after May 2019 suggests that rheumatologists have taken into account the potential VTE risk. These results need to be confirmed by further evidence.
Keywords: JAK inhibitors; rheumatoid arthritis; tolerance; venous thromboembolic risk.
Conflict of interest statement
J.-G.L. reports a research grant from Pfizer. He received honorary fees from Sêmeia. V.G. has received consulting fees from Abbvie, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Galapagos and Sanofi. R.-M.F. is a member of the advisory board at Pfizer, MSD, Abbvie, Janssen, Celltrion, BMS and Sanofi. He received honorary fees from Pfizer, MSD, Abbvie, Janssen, Celltrion, BMS, Sanofi, Lilly, Galapagos, Novartis, Nordic Pharma, Roche-Chugai and UCB. X.D. is a member of the advisory board at Pfizer and UCB. He received honorary fees from Pfizer, UCB, Abbvie, Novartis and MSD. P.P. received honorary fees from Abbvie, MSD, Novartis and Sanofi. Tristan Pascart received honorary fees from Pfizer, BMS, Sanofi, Abbvie and research grants from Chugaï. C.P., V.D., A.N., E.C. and E.H. declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous