Comprehensive Survey of Consensus Docking for High-Throughput Virtual Screening
- PMID: 36615367
- PMCID: PMC9821981
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28010175
Comprehensive Survey of Consensus Docking for High-Throughput Virtual Screening
Abstract
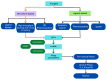
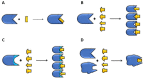
The rapid advances of 3D techniques for the structural determination of proteins and the development of numerous computational methods and strategies have led to identifying highly active compounds in computer drug design. Molecular docking is a method widely used in high-throughput virtual screening campaigns to filter potential ligands targeted to proteins. A great variety of docking programs are currently available, which differ in the algorithms and approaches used to predict the binding mode and the affinity of the ligand. All programs heavily rely on scoring functions to accurately predict ligand binding affinity, and despite differences in performance, none of these docking programs is preferable to the others. To overcome this problem, consensus scoring methods improve the outcome of virtual screening by averaging the rank or score of individual molecules obtained from different docking programs. The successful application of consensus docking in high-throughput virtual screening highlights the need to optimize the predictive power of molecular docking methods.
Keywords: binding site; consensus docking; drug discovery; molecular docking; scoring function; virtual screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Dhasmana A.R., Jahan S.R., Lohani M., Arif J.M. Chapter 19—High-Throughput Virtual Screening (HTVS) of Natural Compounds and Exploration of Their Biomolecular Mechanisms: An In Silico Approach. In: Ahmad M.S., Khan I.A., Chattopadhyay D., editors. New Look to Phytomedicine. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2019. pp. 523–548.
-
- Kontoyianni M. Docking and Virtual Screening in Drug Discovery. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017;1647:255–266. - PubMed
-
- Parker C.N., Bajorath J. Towards Unified Compound Screening Strategies: A Critical Evaluation of Error Sources in Experimental and Virtual High-Throughput Screening. Qsar. Comb. Sci. 2006;25:1153–1161. doi: 10.1002/qsar.200610069. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

