Radiochemical Synthesis of 4-[18F]FluorobenzylAzide and Its Conjugation with EGFR-Specific Aptamers
- PMID: 36615487
- PMCID: PMC9821934
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28010294
Radiochemical Synthesis of 4-[18F]FluorobenzylAzide and Its Conjugation with EGFR-Specific Aptamers
Abstract
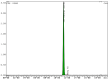
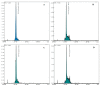
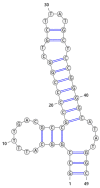
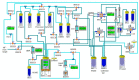
Central nervous system tumors related to gliomas are of neuroectodermal origin and cover about 30% of all primary brain tumors. Glioma is not susceptible to any therapy and surgical attack remains one of the main approaches to its treatment. Preoperative tumor imaging methods, such as positron emission tomography (PET), are currently used to distinguish malignant tissue to increase the accuracy of glioma removal. However, PET is lacking a specific visualization of cells possessing certain molecular markers. Here, we report an application of aptamers to enhancing specificity in imaging tumor cells bearing the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Glioblastoma is characterized by increased EGFR expression, as well as mutations of this receptor associated with active division, migration, and adhesion of tumor cells. Since 2021, EGFR has been included into the WHO classification of gliomas as a molecular genetic marker. To obtain conjugates of aptamers GR20 and GOL1-specific to EGFR, a 4-[18F]fluorobenzylazide radiotracer was used as a synthon. For the production of the synthon, a method of automatic synthesis on an Eckert & Ziegler research module was adapted and modified using spirocyclic iodonium ylide as a precursor. Conjugation of 4-[18F]fluorobenzylazide and alkyne-modified aptamers was carried out using Cu(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) with/without the TBTA ligand. As a result, it was possible to obtain 18F-labelled conjugates with 97% radiochemical purity for [18F]FB-GR20 and 98% for [18F]FB-GOL1. The obtained conjugates can be used for further studies in PET analysis on model animals with grafted glioblastoma.
Keywords: CuAAC; EGFR; PET imaging; iodonium ylides; oligonucleotides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Brown T.J., Brennan M.C., Li M., Church E.W., Brandmeir N.J., Rakszawski K.L., Patel A.S., Rizk E.B., Suki D., Sawaya R., et al. Association of the extent of resection with survival in glioblastoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2016;2:1460–1469. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.1373. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ostrom Q.T., Gittleman H., Liao P., Vecchione-Koval T., Wolinsky Y., Kruchko C., Barnholtz-Sloan J.S. CBTRUS Statistical report: Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2010–2014. Neuro-Oncology. 2017;19((Suppl. S5)):v1–v88. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nox158. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Louis D.N., Perry A., Wesseling P., Brat D.J., Cree I.A., Figarella-Branger D., Hawkins C., Ng H.K., Pfister S.M., Reifenberger G., et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro Oncol. 2021;23:1231–1251. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noab106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

