Chiral Bromonium Salt (Hypervalent Bromine(III)) with N-Nitrosamine as a Halogen-Bonding Bifunctional Catalyst
- PMID: 36615579
- PMCID: PMC9822295
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28010384
Chiral Bromonium Salt (Hypervalent Bromine(III)) with N-Nitrosamine as a Halogen-Bonding Bifunctional Catalyst
Abstract
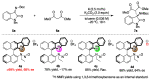
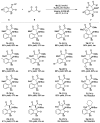
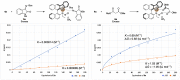
There has been a great focus on halogen-bonding as a unique interaction between electron-deficient halogen atoms with Lewis basic moieties. Although the application of halogen-bonded atoms in organic chemistry has been eagerly researched in these decades, the development of chiral molecules with halogen-bonding functionalities and their utilization in asymmetric catalysis are still in the\ir infancy. We have previously developed chiral halonium salts with amide functionalities, which behaved as excellent catalysts albeit in only two reactions due to the lack of substrate activation abilities. In this manuscript, we have developed chiral halonium salts with an N-nitrosamine moiety and applied them to the Mannich reaction of isatin-derived ketimines with malonic esters. The study focused on our novel bromonium salt catalyst which provided the corresponding products in high yields with up to 80% ee. DFT calculations of the chiral catalyst structure suggested that the high asymmetric induction abilities of this catalyst are due to the Lewis basic role of the N-nitrosamine part. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first catalytic application of N-nitrosamines.
Keywords: N-nitrosamine; asymmetric catalysis; bromonium salt; halogen bonding; hypervalent bromine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Costa P.J. The halogen bond: Nature and applications. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2017;2:20170136. doi: 10.1515/psr-2017-0136. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

