Trends of Medicinal Plant Use over the Last 2000 Years in Central Europe
- PMID: 36616265
- PMCID: PMC9823631
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12010135
Trends of Medicinal Plant Use over the Last 2000 Years in Central Europe
Abstract
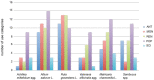
Medicinal plant knowledge in Central Europe can be traced back from the present to antiquity, through written sources. Approximately 100 medicinal plant taxa have a history of continuous use. In this paper, we focus on use patterns over time and the link between historical and traditional uses with the current scientific evidence. We discuss our findings against the backdrop of changing eras and medicinal concepts. Based on use-records from totally 16 historical, popular and scientific herbals, we analyze how use categories of 102 medicinal plant taxa developed over time. Overall, 56 of the 102 taxa maintained continuous use throughout all time periods. For approximately 30% of the continuous uses, scientific evidence supporting their use exists, compared to 11% for recently added uses and 6% for discontinuous uses. Dermatology and gastroenterology are use categories that are relevant across all time periods. They are associated with a high diversity of medicinal taxa and continuously used medicinal species with scientific evidence. Antidotes, apotropaic (protective) magic, and humoral detoxification were important use categories in the past. New applications reflecting biomedical progress and epidemiological challenges are cardiovascular and tonic uses. Changes in medicinal concepts are mirrored in plant use and specifically in changes in the importance of use categories. Our finding supports the concept of social validation of plant uses, i.e., the assumption that longstanding use practice and tradition may suggest efficacy and safety.
Keywords: Central Europe; historical ethnobotany; historical ethnopharmacology; medicinal plants; traditional use.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Clair S. Die Kräutermedizin des Renaissance-Arztes Tabernaemontanus (16. Jh.) und Phytotherapie heute—Was ist geblieben, was hat sich verändert? Schweiz. Z. Ganzheitsmed. 2011;23:46–52. doi: 10.1159/000323387. - DOI
-
- Mayer-Nicolai C. Vergleich der Durch die Historischen Autoren Hildegard von Bingen und Leonhart Fuchs Pflanzlichen Arzneimitteln Zugeschriebenen mit Aktuell Anerkannten Indikationen. Universität Würzburg; Würzburg, Germany: 2008. [(accessed on 22 October 2022)]. Available online: https://nbn-resolving.org/urn:nbn:de:bvb:20-opus-33967.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

