Microwave-Based Subsurface Characterization through a Combined Finite Element and Variable Exponent Spaces Technique
- PMID: 36616765
- PMCID: PMC9823888
- DOI: 10.3390/s23010167
Microwave-Based Subsurface Characterization through a Combined Finite Element and Variable Exponent Spaces Technique
Abstract
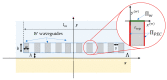
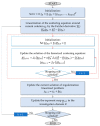
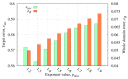
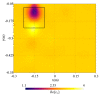
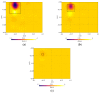
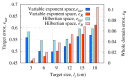
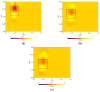
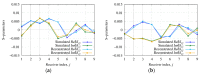
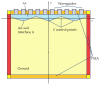
A microwave characterization technique to inspect subsurface scenarios is proposed and numerically assessed in this paper. The approach is based on a combination of finite element electromagnetic modeling and an inversion procedure in Lebesgue spaces with variable exponents. The former allows for description of the measurement system and subsurface scenario with high accuracy, while the latter exploits the adaptive definition of exponent function to achieve improved results in the regularized solution of the inverse scattering problem. The method has been assessed with numerical simulations regarding two-layered environments with both planar and non-planar air-soil interfaces. The results show the capabilities of the method of detecting buried objects in different operative conditions.
Keywords: Lebesgue spaces; finite element; inverse scattering; subsurface imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Persico R. Introduction to Ground Penetrating Radar: Inverse Scattering and Data Processing. John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2014.
-
- Benedetto A., Pajewski L. Civil Engineering Applications of Ground Penetrating Radar. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2015.
-
- Frigui H., Zhang L., Gader P.D. Context-Dependent Multisensor Fusion and Its Application to Land Mine Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010;48:2528–2543. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2039936. - DOI
-
- Pastorino M., Randazzo A. Microwave Imaging Methods and Applications. Artech House; London, UK: 2018.
-
- Salucci M., Oliveri G., Massa A. GPR Prospecting through an Inverse-Scattering Frequency-Hopping Multifocusing Approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015;53:6573–6592. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2444391. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

