An Overview of Fog Data Analytics for IoT Applications
- PMID: 36616797
- PMCID: PMC9824595
- DOI: 10.3390/s23010199
An Overview of Fog Data Analytics for IoT Applications
Abstract
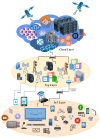
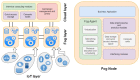
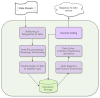
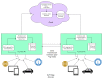
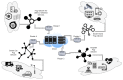
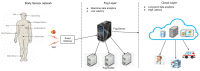
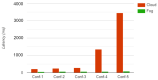
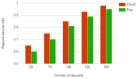
With the rapid growth in the data and processing over the cloud, it has become easier to access those data. On the other hand, it poses many technical and security challenges to the users of those provisions. Fog computing makes these technical issues manageable to some extent. Fog computing is one of the promising solutions for handling the big data produced by the IoT, which are often security-critical and time-sensitive. Massive IoT data analytics by a fog computing structure is emerging and requires extensive research for more proficient knowledge and smart decisions. Though an advancement in big data analytics is taking place, it does not consider fog data analytics. However, there are many challenges, including heterogeneity, security, accessibility, resource sharing, network communication overhead, the real-time data processing of complex data, etc. This paper explores various research challenges and their solution using the next-generation fog data analytics and IoT networks. We also performed an experimental analysis based on fog computing and cloud architecture. The result shows that fog computing outperforms the cloud in terms of network utilization and latency. Finally, the paper is concluded with future trends.
Keywords: Internet of things; artificial intelligence; blockchain; data analytics; fog computing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Atzori L., Iera A., Morabito G. The internet of things: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2010;54:2787–2805. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2010.05.010. - DOI
-
- Nick G. How Many IoT Devices Are There In 2022? More Than Ever! [(accessed on 24 November 2022)]. Available online: https://techjury.net/blog/how-many-iot-devices-are-there/
-
- Farahani B., Firouzi F., Chang V., Badaroglu M., Constant N., Mankodiya K. Towards fog-driven IoT eHealth: Promises and challenges of IoT in medicine and healthcare. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018;78:659–676. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2017.04.036. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

