Current Technologies for Detection of COVID-19: Biosensors, Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Medical Things (IoMT): Review
- PMID: 36617023
- PMCID: PMC9824404
- DOI: 10.3390/s23010426
Current Technologies for Detection of COVID-19: Biosensors, Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Medical Things (IoMT): Review
Abstract
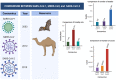
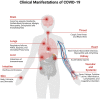
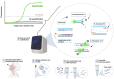
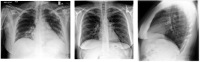
Despite the fact that COVID-19 is no longer a global pandemic due to development and integration of different technologies for the diagnosis and treatment of the disease, technological advancement in the field of molecular biology, electronics, computer science, artificial intelligence, Internet of Things, nanotechnology, etc. has led to the development of molecular approaches and computer aided diagnosis for the detection of COVID-19. This study provides a holistic approach on COVID-19 detection based on (1) molecular diagnosis which includes RT-PCR, antigen-antibody, and CRISPR-based biosensors and (2) computer aided detection based on AI-driven models which include deep learning and transfer learning approach. The review also provide comparison between these two emerging technologies and open research issues for the development of smart-IoMT-enabled platforms for the detection of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Internet of Medical Things (IoMT); artificial intelligence; biosensors; computer-aided detection (CAD).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

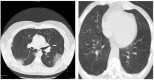
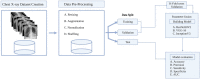
References
-
- Hamza A., Khan M.A., Wang S.H., Alhaisoni M., Alharbi M., Hussein H.S., Alshazly H., Kim Y.J., Cha J. COVID-19 classification using chest X-ray images based on fusion-assisted deep Bayesian optimization and Grad-CAM visualization. Front. Public Health. 2022;10:1046296. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1046296. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Khan M.A., Alhaisoni M., Nazir M., Alqahtani A., Binbusayyis A., Alsubai S., Nam Y., Kang B.G. A Healthcare System for COVID19 Classification Using Multi-Type Classical Features Selection. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2023;74:1393–1412. doi: 10.32604/cmc.2023.032064. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

