Safety and antitumor activity of GD2-Specific 4SCAR-T cells in patients with glioblastoma
- PMID: 36617554
- PMCID: PMC9827625
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-022-01711-9
Safety and antitumor activity of GD2-Specific 4SCAR-T cells in patients with glioblastoma
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to validate whether infusion of GD2-specific fourth-generation safety-designed chimeric antigen receptor (4SCAR)-T cells is safe and whether CAR-T cells exert anti-glioblastoma (GBM) activity.
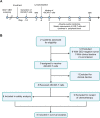
Methods: A total of eight patients with GD2-positive GBM were enrolled and infused with autologous GD2-specific 4SCAR-T cells, either through intravenous administration alone or intravenous combined with intracavitary administration.
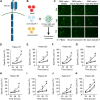
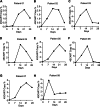
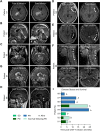
Results: 4SCAR-T cells expanded for 1-3 weeks and persisted at a low frequency in peripheral blood. Of the eight evaluable patients, four showed a partial response for 3 to 24 months, three had progressive disease for 6 to 23 months, and one had stable disease for 4 months after infusion. For the entire cohort, the median overall survival was 10 months from the infusion. GD2 antigen loss and infiltrated T cells were observed in the tumor resected after infusion.
Conclusion: Both single and combined infusions of GD2-specific 4SCAR-T cells in targeting GBM were safe and well tolerated, with no severe adverse events. In addition, GD2-specific 4SCAR-T cells partially mediate antigen loss and activate immune responses in the tumor microenvironment. Validation of our findings in a larger prospective trial is warranted.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03170141 . Registered 30 May 2017.
Keywords: 4SCAR-T; GBM; GD2; Safety; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, Van Den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B, Belanger K. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:459–66. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70025-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

