Gymnema inodorum Leaf Extract Improves Cardiac Function in Experimental Mice Infected with Plasmodium Berghei
- PMID: 36617811
- PMCID: PMC9834418
- DOI: 10.1177/2515690X221150526
Gymnema inodorum Leaf Extract Improves Cardiac Function in Experimental Mice Infected with Plasmodium Berghei
Abstract
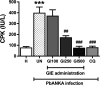
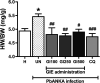
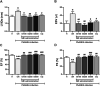
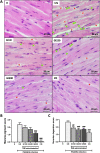
Malaria-associated cardiac injury has been reported to be the primary cause of death due to severe malaria. The discovery of substances showing a protective effect on cardiac injury during malaria infection is urgently needed. Hence, the purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of Gymnema inodorum leaf extract (GIE) on cardiac function in mice infected with Plasmodium berghei. ICR mice were treated with 1 × 107 infected red blood cells of P. berghei ANKA (PbANKA), administered orally with GIE in 100, 250 and 500 mg/kg body weight of mice. Creatine phosphokinase (CPK) and echocardiography were carried out. It was found that CPK and heart-weight to body-weight (HW/BW) ratios were significantly higher in untreated mice than the healthy control. Moreover, impaired cardiac function in the untreated group was observed as indicated by changes in echocardiography. Interestingly, GIE exerted a protective effect on cardiac injury induced by PbANKA infection. Our results demonstrated that the parasitemia percentage, CPK, HW/BW ratio, and echocardiography in GIE treated mice were improved. However, there was no significant difference between GIE dosages. Therefore, GIE possessed a cardio-protective effect during malaria infection in mice.
Keywords: cardiac function; gymnema inodorum; malaria; pbANKA.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic antimalarial treatment of Plasmodium berghei infection in mice with dihydroartemisinin and Gymnema inodorum leaf extract.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Jan 23;23(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-03850-y. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 36690988 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Gymnema inodorum Leaf Extract on the Alteration of Blood Coagulation Parameters and Platelet Count in Plasmodium berghei-Infected Mice.J Parasitol Res. 2022 Mar 11;2022:4225682. doi: 10.1155/2022/4225682. eCollection 2022. J Parasitol Res. 2022. PMID: 35310010 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Gymnema inodorum Leaf Extract on Plasmodium berghei-Induced Hypoglycemia, Dyslipidemia, Liver Damage, and Acute Kidney Injury in Experimental Mice.J Parasitol Res. 2021 Sep 12;2021:1896997. doi: 10.1155/2021/1896997. eCollection 2021. J Parasitol Res. 2021. PMID: 34552764 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Role of Gymnema inodorum Leaf Extract Treatment in Hematological Parameters in Mice Infected with Plasmodium berghei.J Trop Med. 2021 Jun 28;2021:9989862. doi: 10.1155/2021/9989862. eCollection 2021. J Trop Med. 2021. PMID: 34257672 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Antimalarial Potential of Aqueous Crude Gymnema Inodorum Leaf Extract against Plasmodium berghei Infection in Mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Apr 27;2021:9932891. doi: 10.1155/2021/9932891. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33995550 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The cytoprotective effect of Gymnema inodorum leaf extract against hypoxia-induced cardiomyocytes injury.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 6;10(15):e35846. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35846. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170335 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-malarial and haematological evaluation of the ethanolic, ethyl acetate and aqueous fractions of Chromolaena odorata.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Nov 9;23(1):402. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04200-8. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37946127 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of phytochemicals and antioxidant activities in Gymnema inodorum leaf extracts.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 2;10(1):e23175. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23175. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38163201 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Benefits of Gymnema inodorum Leaf Extract in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Under Peroxynitrite Stress.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Apr 1;14(4):427. doi: 10.3390/antiox14040427. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40298831 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health O. World malaria report 2021. World Health Organization, 2021.
-
- Kotlyar S, Olupot-Olupot P, Nteziyaremye J, et al.. Assessment of myocardial function and injury by echocardiography and cardiac biomarkers in African children with severe plasmodium falciparum malaria. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2018; 19(3): 179-185. DOI: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000001411 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

