Identification and characterization of RNA binding sites for (p)ppGpp using RNA-DRaCALA
- PMID: 36617997
- PMCID: PMC9881157
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkac1224
Identification and characterization of RNA binding sites for (p)ppGpp using RNA-DRaCALA
Abstract
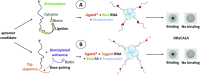
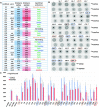
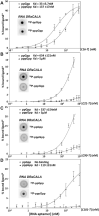
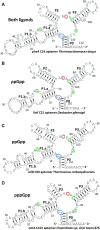
Ligand-binding RNAs (RNA aptamers) are widespread in the three domains of life, serving as sensors of metabolites and other small molecules. When aptamers are embedded within RNA transcripts as components of riboswitches, they can regulate gene expression upon binding their ligands. Previous methods for biochemical validation of computationally predicted aptamers are not well-suited for rapid screening of large numbers of RNA aptamers. Therefore, we utilized DRaCALA (Differential Radial Capillary Action of Ligand Assay), a technique designed originally to study protein-ligand interactions, to examine RNA-ligand binding, permitting rapid screening of dozens of RNA aptamer candidates concurrently. Using this method, which we call RNA-DRaCALA, we screened 30 ykkC family subtype 2a RNA aptamers that were computationally predicted to bind (p)ppGpp. Most of the aptamers bound both ppGpp and pppGpp, but some strongly favored only ppGpp or pppGpp, and some bound neither. Expansion of the number of biochemically verified sites allowed construction of more accurate secondary structure models and prediction of key features in the aptamers that distinguish a ppGpp from a pppGpp binding site. To demonstrate that the method works with other ligands, we also used RNA DRaCALA to analyze aptamer binding by thiamine pyrophosphate.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Structures of two aptamers with differing ligand specificity reveal ruggedness in the functional landscape of RNA.Elife. 2018 Jun 7;7:e36381. doi: 10.7554/eLife.36381. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29877798 Free PMC article.
-
Differential binding of ppGpp and pppGpp to E. coli RNA polymerase: photo-labeling and mass spectral studies.Genes Cells. 2015 Dec;20(12):1006-16. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12304. Epub 2015 Oct 8. Genes Cells. 2015. PMID: 26606426
-
Assessing RNA interactions with proteins by DRaCALA.Methods Enzymol. 2014;549:489-512. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-801122-5.00021-0. Methods Enzymol. 2014. PMID: 25432762
-
Structural Changes in Aptamers are Essential for Synthetic Riboswitch Engineering.J Mol Biol. 2022 Sep 30;434(18):167631. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2022.167631. Epub 2022 May 17. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35595164 Review.
-
Tapping the potential of synthetic riboswitches: reviewing the versatility of the tetracycline aptamer.RNA Biol. 2023 Jan;20(1):457-468. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2023.2234732. RNA Biol. 2023. PMID: 37459466 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of (p)ppGpp metabolism and signaling using a dynamic luminescent reporter.PLoS Genet. 2025 Aug 22;21(8):e1011691. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011691. eCollection 2025 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2025. PMID: 40845056 Free PMC article.
-
Sound the (Smaller) Alarm: The Triphosphate Magic Spot Nucleotide pGpp.Infect Immun. 2023 Apr 18;91(4):e0043222. doi: 10.1128/iai.00432-22. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Infect Immun. 2023. PMID: 36920208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How to quantify magic spots - a brief overview of (p)ppGpp detection and quantitation methods.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Mar 25;12:1574135. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1574135. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40201240 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ellington A.D., Szostak J.W.. Selection in vitro of single-stranded DNA molecules that fold into specific ligand-binding structures. Nature. 1992; 355:850–852. - PubMed
-
- Winkler W., Nahvi A., Breaker R.R.. Thiamine derivatives bind messenger RNAs directly to regulate bacterial gene expression. Nature. 2002; 419:952–956. - PubMed
-
- Winkler W.C., Nahvi A., Roth A., Collins J.A., Breaker R.R.. Control of gene expression by a natural metabolite-responsive ribozyme. Nature. 2004; 428:281–286. - PubMed
-
- Nahvi A., Sudarsan N., Ebert M.S., Zou X., Brown K.L., Breaker R.R.. Genetic control by a metabolite binding mRNA. Chem. Biol. 2002; 9:1043–1049. - PubMed
-
- Mironov A.S., Gusarov I., Rafikov R., Lopez L.E., Shatalin K., Kreneva R.A., Perumov D.A., Nudler E.. Sensing small molecules by nascent RNA: a mechanism to control transcription in bacteria. Cell. 2002; 111:747–756. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

