Comparative study of differentiating human pluripotent stem cells into vascular smooth muscle cells in hydrogel-based culture methods
- PMID: 36618488
- PMCID: PMC9798140
- DOI: 10.1016/j.reth.2022.12.001
Comparative study of differentiating human pluripotent stem cells into vascular smooth muscle cells in hydrogel-based culture methods
Abstract
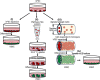
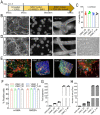
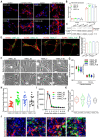
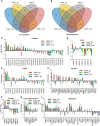
Vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), which provides structural integrity and regulates the diameter of vasculature, are of great potential for modeling vascular-associated diseases and tissue engineering. Here, we presented a detailed comparison of differentiating human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) into VSMCs (hPSCs-VSMCs) in four different culture methods, including 2-dimensional (2D) culture, 3-dimensional (3D) PNIPAAm-PEG hydrogel culture, 3-dimensional (3D) alginate hydrogel culture, and transferring 3-dimensional alginate hydrogel culture to 2-dimensional (2D) culture. Both hydrogel-based culture methods could mimic in vivo microenvironment to protect cells from shear force, and avoid cells agglomeration, resulting in the extremely high culture efficiency (e.g., high viability, high purity and high yield) compared with 2D culture. We demonstrated hPSC-VSMCs produced from hydrogel-based culture methods had better contractile phenotypes and the potential of vasculature formation. The transcriptome analysis showed the hPSC-VSMCs derived from hydrogel-based culture methods displayed more upregulated genes in vasculature development, angiogenesis and blood vessel development, extracellular matrix compared with 2D culture. Taken together, hPSC-VSMCs produced from hydrogel-based culture system could be applied in various biomedical fields, and further indicated the suitable development of alginate hydrogel for industrial production by taking all aspects into consideration.
Keywords: Alginate hydrogel fiber; Human pluripotent stem cells; Industrial production; PNIPAAm-PEG hydrogel; Vascular smooth muscle cells.
© 2022 The Japanese Society for Regenerative Medicine. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparative Study of Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Endothelial Cells in Hydrogel-Based Culture Systems.ACS Omega. 2021 Mar 2;6(10):6942-6952. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c06187. eCollection 2021 Mar 16. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 33748608 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiating human pluripotent stem cells into vascular smooth muscle cells in three dimensional thermoreversible hydrogels.Biomater Sci. 2018 Dec 18;7(1):347-361. doi: 10.1039/c8bm01128a. Biomater Sci. 2018. PMID: 30483691
-
Engineered Microenvironment for Manufacturing Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells.Stem Cell Reports. 2019 Jan 8;12(1):84-97. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2018.11.009. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Stem Cell Reports. 2019. PMID: 30527760 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation from human stem/progenitor cells.Methods. 2016 May 15;101:85-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.12.004. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Methods. 2016. PMID: 26678794 Review.
-
Deriving vascular smooth muscle cells from mesenchymal stromal cells: Evolving differentiation strategies and current understanding of their mechanisms.Biomaterials. 2017 Nov;145:9-22. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.08.028. Epub 2017 Aug 15. Biomaterials. 2017. PMID: 28843066 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Alginate-Based Hydrogels for Cell Transplantation Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Mar 27;16(4):469. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16040469. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38675129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular Toxicity in Cancer Therapy: Protecting the Heart while Combating Cancer.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2024 Sep;26(9):953-971. doi: 10.1007/s11886-024-02099-2. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39042344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements and Challenges in Hydrogel Engineering for Regenerative Medicine.Gels. 2024 Mar 30;10(4):238. doi: 10.3390/gels10040238. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38667657 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

