Lead-vanadate sorbents for iodine trapping and their conversion into an iodoapatite-based conditioning matrix
- PMID: 36618862
- PMCID: PMC9811818
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1085868
Lead-vanadate sorbents for iodine trapping and their conversion into an iodoapatite-based conditioning matrix
Abstract
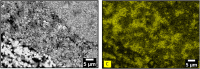
New lead-vanadate based sorbents were synthesized with the aim to entrap and confine gaseous iodine in off-gas streams coming from reprocessing facilities of spent nuclear fuel. Their synthesis relies on the shaping of a lead-vanadate, lead sulfide and alginic acid mix as millimetric beads. These beads were calcined between 220°C and 500°C to remove organic alginic compounds template. However, according to the calcination temperature, lead sulfide could be partially oxidized, limiting iodine loading capacity. A compromise temperature between 290°C and 350°C was found to remove most of the alginic acid template and avoiding lead sulfide oxidation. These sorbents were tested for iodine trapping in static conditions at 60°C. They performed well with a sorption capacity up to 155 mg.g-1 by forming PbI2. Furthermore, these iodine-loaded sorbents could be easily converted into an iodine-containing lead-vanadate apatite matrix by spark plasma sintering. A dense sample was produced for a sintering temperature of 500°C under 70 MPa. Such a material could be suitable for radioactive iodine conditioning in deep geological disposal. Finally, lead-vanadate sorbents could provide an easy way to entrap and confine radioactive iodine from off-gas streams into a durable material within a few steps.
Keywords: apatite; filter; iodine; off-gas; waste disposal.
Copyright © 2022 Pénélope, Campayo, Fournier, Le Gallet, Gossard and Grandjean.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Abasalizadeh F., Moghaddam S. V., Alizadeh E., Akbari E., Kashani E., Fazljou S. M. B., et al. (2020). Alginate-based hydrogels as drug delivery vehicles in cancer treatment and their applications in wound dressing and 3D bioprinting. J. Biol. Eng. 14, 8. 10.1186/s13036-020-0227-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Audubert F. (1995). Mise au point d’une matrice apatitique pour le confinement de l’iode 129. These de doctorat. Toulouse: INPT. [Internet][cited 2022 Oct 6]. Available from: https://www.theses.fr/1995INPT001G .
-
- Audubert F., Savariault J. M., Lacout J. L. (1999). Pentalead tris(vanadate) iodide, a defect vanadinite-type compound. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C 55 (3), 271–273. 10.1107/s0108270198005034 - DOI
-
- Azambre B., Chebbi M., Leroy O., Cantrel L. (2018). Effects of zeolitic parameters and irradiation on the retention properties of silver zeolites exposed to molecular iodine. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 57 (5), 1468–1479. 10.1021/acs.iecr.7b03579 - DOI
-
- Bertelsen E. R., Antonio M. R., Jensen M. P., Shafer J. C. (2022). Electrochemistry of PUREX: R is for reduction and ion transfer. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 40 (1–2), 64–85. 10.1080/07366299.2021.1920674 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

