Ultrasonic optic nerve sheath diameter could improve the prognosis of acute ischemic stroke in the intensive care unit
- PMID: 36618944
- PMCID: PMC9816399
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1077131
Ultrasonic optic nerve sheath diameter could improve the prognosis of acute ischemic stroke in the intensive care unit
Abstract
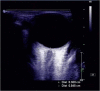
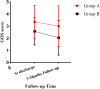
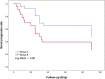
Objectives: Stroke patients with high intracranial pressure (ICP) may have poor prognosis. Non-invasive ultrasonic optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) could evaluate increased ICP. To investigate whether ONSD is valuable for prognosis of patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS). Methods: AIS receiving intensive care were recruited with the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score. Patients in group A underwent ultrasonic ONSD to assess ICP voluntarily, whereas group B without ONSD. Patients were followed up at discharge and once a week for 3 months with Glasgow Outcome Scale (GOS) score (four to five scores indicated good prognosis and one to three scores indicated poor prognosis). Results: Forty-nine patients were included. GCS scores did not differ significantly between groups A (26 patients) and B (8 ± 3 vs. 7 ± 3, p < 0.05). In group A, ONSD was 5.01 ± 0.48 mm, which correlated with GCS score (p < 0.05). At discharge, the GOS score was higher in group A than in group B (3.35 ± 1.35 vs. 2.57 ± 1.121, p = 0.034). The proportion of patients with a good prognosis was higher in group A than in group B (46.2% vs. 13.0%, p = 0.006). At discharge and after 3 months of follow-up, ONSD at admission was correlated with the GOS score in group A (r = -0.648 [p < 0.05] and -0.731 [p < 0.05], respectively). After 3 months of follow-up, the GOS score was higher in group A than group B (3.00 ± 1.673 vs. 2.04 ± 1.430, p < 0.05). The proportion of patients with a good prognosis was higher in group A than in group B (46.2% vs. 21.2%, p = 0.039). The Kaplan-Meier curve showed a higher rate of good prognosis in group A than in group B. ONSD (p < 0.05) was an independent predictor of poor prognosis. Conclusion: Non-invasive ultrasonic ONSD could be useful in improving the prognosis of patients with AIS receiving intensive care.
Keywords: intracranial pressure; non-invasive; optic nerve sheath diameter; prognosis; stroke; ultrasonic measurement.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Wang, Meng, Fan, Zhang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The clinical and prognostic values of optic nerve sheath diameter and optic nerve sheath diameter/eyeball transverse diameter ratio in comatose patients with supratentorial lesions.BMC Neurol. 2021 Jul 2;21(1):259. doi: 10.1186/s12883-021-02285-7. BMC Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34215217 Free PMC article.
-
Role of serial ultrasonic optic nerve sheath diameter monitoring in head injury.Neurochirurgie. 2017 Dec;63(6):444-448. doi: 10.1016/j.neuchi.2017.06.001. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Neurochirurgie. 2017. PMID: 29122307
-
Diagnostic and prognostic value of the optic nerve sheath diameter with respect to the intracranial pressure and neurological outcome of patients following hemicraniectomy.BMC Neurol. 2018 Dec 5;18(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s12883-018-1202-5. BMC Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30518315 Free PMC article.
-
Optic nerve sheath diameter: present and future perspectives for neurologists and critical care physicians.Neurol Sci. 2019 Dec;40(12):2447-2457. doi: 10.1007/s10072-019-04015-x. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Neurol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31367861 Review.
-
Ultrasonic measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter: a non-invasive surrogate approach for dynamic, real-time evaluation of intracranial pressure.Br J Ophthalmol. 2019 Apr;103(4):437-441. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2018-312934. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Br J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 30361274 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The correlation of optic nerve sheath diameter with clinical outcomes in patients undergoing decompressive craniectomy for cerebral infarction.Surg Neurol Int. 2025 May 16;16:184. doi: 10.25259/SNI_327_2025. eCollection 2025. Surg Neurol Int. 2025. PMID: 40469317 Free PMC article.
-
Optic nerve sheath diameters in nontraumatic brain injury: A scoping review and role in the intensive care unit.World J Crit Care Med. 2024 Sep 9;13(3):97205. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v13.i3.97205. eCollection 2024 Sep 9. World J Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 39253313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chinese Society of Neurology (2018). Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of acute ischemic stroke 2018. Zhong Hua Neurology Chin. J. ] 51 (9), 666–682. 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7876.2018.09.004 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

